Zooko's triangle
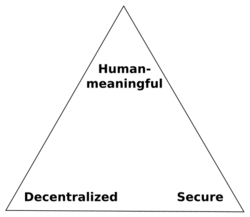
Zooko's triangle is a trilemma of three properties that some people consider desirable for names of participants in a network protocol:[1]
- Human-meaningful: Meaningful and memorable (low-entropy) names are provided to the users.
- Secure: The amount of damage a malicious entity can inflict on the system should be as low as possible.
- Decentralized: Names correctly resolve to their respective entities without the use of a central authority or service.
Overview
Zooko Wilcox-O'Hearn conjectured that no single kind of name can achieve more than two. For example: DNSSec offers a human-meaningful, secure naming scheme, but is not decentralized as it relies on trusted root-servers; .onion addresses and bitcoin addresses are secure and decentralized but not human-meaningful; and I2P uses name translation services which are secure (as they run locally) and provide human-meaningful names - but fail to provide unique entities when used globally in a decentralised network without authorities.[lower-alpha 1]
Solutions
Several systems that exhibit all three properties of Zooko's triangle include:
- Computer scientist Nick Szabo's paper "Secure Property Titles with Owner Authority" illustrated that all three properties can be achieved up to the limits of Byzantine fault tolerance.[2]
- Activist Aaron Swartz described a naming system based on Bitcoin employing Bitcoin's distributed blockchain as a proof-of-work to establish consensus of domain name ownership.[3] These systems remain vulnerable to Sybil attack,[4] but are secure under Byzantine assumptions.
- Theoretician Curtis Yarvin implemented a decentralized version of IP addresses in Urbit that hash to four-syllable, human-readable names.[5]
Several platforms implement refutations of Zooko's conjecture, including: Twister (which use Swartz' system with a bitcoin-like system), Blockstack (separate blockchain), Namecoin (separate blockchain), LBRY (separate blockchain - content discovery, ownership, and peer-to-peer file-sharing),[citation needed] Monero, OpenAlias,[6] Ethereum Name Service, and the Handshake Protocol.[7]
See also
- Petname
- GNU Name System
- CAP theorem
Notes
- ↑ Zooko Wilcox-O'Hearn has since deleted the original blogpost
References
- ↑ Zooko Wilcox-O'Hearn. "Names: Decentralized, Secure, Human-Meaningful: Choose Two". http://zooko.com/distnames.html.
- ↑ Nick Szabo, Secure Property Titles , 1998
- ↑ Aaron Swartz, Squaring the Triangle: Secure, Decentralized, Human-Readable Names , Aaron Swartz, 6 January 2011
- ↑ Dan Kaminsky, Spelunking the Triangle: Exploring Aaron Swartz’s Take On Zooko’s Triangle , 13 January 2011
- ↑ (in en) Curtis Yarvin: Urbit- A Clean Slate Functional Operating Stack - λC 2016, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bTisf4oxIFo, retrieved 2022-07-09
- ↑ Monero core team (2014-09-19). "OpenAlias". http://openalias.org/.
- ↑ Director of The Handshake Project (2021-07-12). "Handshake". https://handshake.org/.
External links
- Zooko Wilcox-O'Hearn, Names: Decentralized, Secure, Human-Meaningful: Choose Two – the essay highlighting this difficulty
- Marc Stiegler, An Introduction to Petname Systems – a clear introduction
- Nick Szabo, Secure Property Titles – argues that all three properties can be achieved up to the limits of Byzantine fault tolerance.
- Bob Wyman, The Persistence of Identity (Updating Zooko's Pyramid)
- Paul Crowley, Squaring Zooko's Triangle
- Aaron Swartz, Squaring the Triangle using a technique from Bitcoin
 |
