Biology:Myogenic determination factor 5
| Myf5 domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Myf5 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF12232 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR022032 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Basic domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
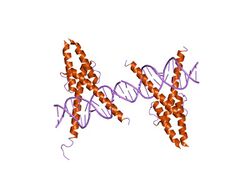 crystal structure of myod bhlh domain bound to dna: perspectives on dna recognition and implications for transcriptional activation | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Basic | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF01586 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR002546 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00038 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1mdy / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, the myogenic determination factor 5 proteins are a family of proteins found in eukaryotes. This family includes the Myf5 protein, which is responsible for directing cells to the skeletal myocyte lineage during development. Myf5 is likely to act in a similar way to the other MRF4 proteins such as MyoD which perform the same function. These are histone acetyltransferases and histone deacetylases which activate and repress genes involved in the myocyte lineage.
Myogenic determination factor 5 proteins contain three conserved protein domains. A C-terminal Myf5 domain, a central basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) domain and an N-terminal basic domain. The bHLH region mediates specific DNA binding.[1] With 12 residues of the basic domain involved in DNA binding.[2] The basic domain forms an extended alpha helix in the structure.
References
- ↑ "The basic domain of myogenic basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) proteins is the novel target for direct inhibition by another bHLH protein, Twist". Mol. Cell. Biol. 17 (11): 6563–73. November 1997. doi:10.1128/mcb.17.11.6563. PMID 9343420.
- ↑ "Combinatorial control of muscle development by basic helix-loop-helix and MADS-box transcription factors". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93 (18): 9366–73. September 1996. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.18.9366. PMID 8790335. Bibcode: 1996PNAS...93.9366M.
 |

