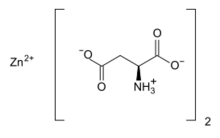
Chemistry:Zinc L-aspartate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Zinc (2S)-2-amino-4-hydroxy-4-oxobutanoate
| |
| Other names
Zinc aspartate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H12N2O8Zn | |
| Molar mass | 329.59848 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Density | Solid |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Zinc l-aspartate, often simply called zinc aspartate, is a chelated zinc supplement. Zinc aspartate is a salt of zinc with the amino acid aspartic acid.
Chemical properties
Zinc aspartate is a white crystalline powder. It is soluble in dilute hydrochloric acid and insoluble in water.[1]
Bioavailability
There are no specific bioavailability studies that were made available on this dietary mineral. It is assumed that the reported solubility of zinc aspartate in diluted hydrochloric acid will allow its dissociation and absorption in the stomach. However, it was not clear if further absorption could take place in the intestine considering its reported insolubility in water.[2]
Hazards
Potential acute health effects may include skin and eye irritation. If inhaled, it can cause lung irritation.
See also
References
- ↑ Technical dossier, 2005f[clarification needed]
- ↑ "SCIENTIFIC OPINION. Magnesium aspartate, potassium aspartate, magnesium potassium aspartate, calcium aspartate, zinc aspartate, and copper aspartate as sources for magnesium, potassium, calcium, zinc, and copper added for nutritional purposes to food supplements". The EFSA Journal 883: 1–23. November 2008. http://www.efsa.europa.eu/EFSA/Scientific_Opinion/ans_ej883_Magnesium_Aspartate_op_en,3.pdf?ssbinary=true. Retrieved 2010-02-01.
 |

