Chemistry:Dioxalin
From HandWiki
Revision as of 17:18, 29 June 2021 by imported>MedAI (add)
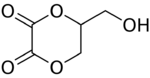
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5-(Hydroxymethyl)-1,4-dioxane-2,3-dione
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H6O5 | |
| Molar mass | 146.098 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Dioxalin is a reaction product of glycerol with oxalic acid at 533 K. Its IUPAC name is 5-(hydroxymethyl)-1,4-dioxane-2,3-dione. Dioxalin readily loses two molecules of carbon dioxide at this high temperature to form allyl alcohol and therefore offers a method for conversion of glycerol to allyl alcohol.[1][2][3]
References
- ↑ Chattaway, Frederick Daniel (1915). "XLVII.—The preparation of allyl alcohol". J. Chem. Soc., Trans. 107: 407–410. doi:10.1039/CT9150700407. https://zenodo.org/record/2475515.
- ↑ Coffey, Samuel; Ward, Charles Frederick (1921). "CXLVIII.—The preparation of some allyl compounds". J. Chem. Soc., Trans. 119: 1301–1306. doi:10.1039/CT9211901301. https://zenodo.org/record/1670183.
- ↑ Arora, Amit (2006) (in en). Carbohydrates and Proteins. Discovery Publishing House. p. 48. ISBN 978-81-8356-178-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=9bSz1ZkJ41AC&pg=PA48.
 |

