Chemistry:4H-Quinolizine
From HandWiki
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H9N | |
| Molar mass | 131.178 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
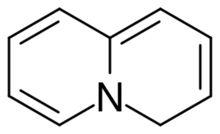
4H-Quinolizine is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C
9H
9N. The location of the ninth hydrogen atom defines the isomer as 4H-. The 2H-, 3H- isomers are also theoretically possible. None have been isolated, so these compounds remain of theoretical interest.[1] These compounds structurally resemble quinoline but with nitrogen at one of the two ring fusion sites. Quinolizines feature tertiary amine at the bridge site. Although quinolizines are elusive, their saturated derivatives quinolizidines C
9H
17N are well known, being found in several alkaloids. Another class of stable derivatives are the quinolizinium cations C
9H
8N+
, resulting from the formal removal of hydride from quinolizines.
References
- ↑ Modern Heterocyclic Chemistry (First ed.). Wiley-VCH. 2011.
 |

