Chemistry:Quinolizinium
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
pyrido[1,2-a]pyridinium
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1423269 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
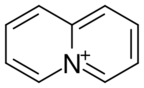
| C 9H 8N+ | |
| Appearance | colorless |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
4H-Quinolizine |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Quinolizinium refers to the heterocyclic cation with the formula C
9H
8N+
. The cation is isoelectronic and nearly isostructural with naphthalene, the difference being the replacement of one of the two carbons at the fusion positions with N+. The parent quinolizine has not been isolated but salts of these aromatic quinolizinium compounds are well known. Several syntheses begin with 2-substituted pyridines and involve N-alkylation and various dehydrogenation reactions.[1] The quinolizinium core is represented in the berberine family of natural products.[2] It is formally derived from the elusive quinolizines by hydrde abstraction. According to X-ray crystallography of the hexafluorophosphate salt, which is colorless, C
9H
8N+
is planar.[3]
Reactions
Being a cation, quinolinizium resists electrophilic attack, although it can be brominated. Catalytic hydrogenation gives quinolizidine.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Julio Alvarez-Builla, ed (2011). Modern Heterocyclic Chemistry. Wiley-VCH.
- ↑ Grycová, Lenka; Dostál, Jiří; Marek, Radek (2007). "Quaternary protoberberine alkaloids". Phytochemistry 68 (2): 150–175. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.10.004. PMID 17109902.
- ↑ Sato, Kiyoshi; Arai, Sadao; Yamagishi, Takamichi; Tanase, Tomoaki (2001). "Quinolizinium Hexafluorophosphate". Acta Crystallographica Section C Crystal Structure Communications 57 (2): 174–175. doi:10.1107/S0108270100015742. PMID 11173443.
 |

