Biology:Equatorial dog-faced bat
| Equatorial dog-faced bat | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Molossidae |
| Genus: | Molossops |
| Species: | M. aequatorianus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Molossops aequatorianus Cabrera, 1917
| |
| |
The equatorial dog-faced bat (Molossops aequatorianus) is a species of bat in the family Molossidae. It is endemic to Ecuador. They are found in dry, tropical forests. The species is now endangered. The equatorial dog-faced bat feeds on insects.[1]
Discovery and etymology
This species was discovered by Spanish zoologist Marcos Jiménez de la Espada in November 1864. Espada encountered four females in Babahoyo, Ecuador near the Guayas River in the crack of an old tree, roosting with harmless serotine bats. It was described by Ángel Cabrera in 1917.[2] Its species name aequatorianus is derived from the Latin word aequatoriensis, meaning "Ecuadorian."
Range and habitat
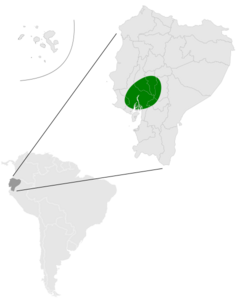
This species is found in dry, tropical forests in west central Ecuador. It has only been found in two locations.[1]
Conservation
The IUCN assessed this species as vulnerable in 1996 and 2008. In 2016, its status was revised to endangered. They are listed as endangered because they occur at fewer than five locations, and a decline is projected in their area and quality of habitat. Its extent of occurrence is estimated at 4,000 km2 (1,500 sq mi). Threats facing this species include habitat destruction, as their habitat is being converted for agricultural usage. Populations that occur in swampy areas are under threat from aquaculture.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Tirira, D. (2016). "Molossops aequatorianus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T13638A22109325. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T13638A22109325.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/13638/22109325.
- ↑ Cabrera, Ángel (1917). Mamíferos del viaje al Pacífico verificado de 1862 a 1865 por una comisión de naturalistas enviada por el gobierno español. Madrid: Junta para Ampliación de Estudios e Investigaciones Científicas. pp. 19–20. ISBN 0259170216. http://simurg.bibliotecas.csic.es/viewer/fullscreen/CSIC000268362/22/.
Wikidata ☰ Q1833512 entry


