Chemistry:Carbomethoxymethylenetriphenylphosphorane
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methyl (triphenyl-λ5-phosphanylidene)acetate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H301, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P321, P330, P362+364Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
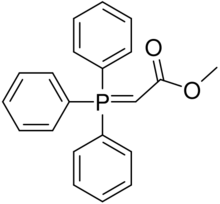
Carbomethoxymethylenetriphenylphosphorane is a chemical compound used in organic syntheses. It contains a phosphorus atom bound to three phenyl groups, and doubly bound to the alpha position of methyl acetate. It undergoes a Wittig reaction.[1] It is used in the Vitamin B12 total synthesis.
Production
Carbomethoxymethylenetriphenylphosphorane can be made via a multistep reaction using bromoacetic acid, dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, and triphenylphosphine. This makes a phosphonium salt, which is converted to the final product by sodium carbonate in water.[1]
Reactions
Carbomethoxymethylenetriphenylphosphorane reacts with aldehydes to give a two carbon atom extension. The carbomethoxymethylene group replaces the oxygen of the aldehyde to give a trans- double bond.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Keck, Gary E.; Boden, Eugene P.; Mabury, Scott A. (March 1985). "A useful Wittig reagent for the stereoselective synthesis of trans-.alpha.,.beta.-unsaturated thiol esters". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 50 (5): 709–710. doi:10.1021/jo00205a036.
 |

