Chemistry:Bromoacetic acid
From HandWiki
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Bromoacetic acid | |||
| Other names
2-Bromoacetic acid
Bromoethanoic acid α-Bromoacetic acid Monobromoacetic acid Carboxymethyl bromide UN 1938 | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 506167 | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H3BrO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 138.948 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White to light yellow crystalline solid | ||
| Density | 1.934 g/mL | ||
| Melting point | 49 to 51 °C (120 to 124 °F; 322 to 324 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 206 to 208 °C (403 to 406 °F; 479 to 481 K) | ||
| polar organic solvents | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.86[1] | ||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.4804 (50 °C, D) | ||
| Structure | |||
| Hexagonal or orthorhombic | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |    
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
| H301, H311, H314, H317, H331, H400 | |||
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P273, P280, P301+310, P301+330+331, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P311, P312, P321, P322, P330, P333+313, P361, P363, P391, P403+233 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
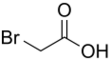
Bromoacetic acid is the chemical compound with the formula CH2BrCO2H. This colorless solid is a relatively strong alkylating agent. Bromoacetic acid and its esters are widely used building blocks in organic synthesis, for example, in pharmaceutical chemistry.
The compound is prepared by bromination of acetic acid, such as by a Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky reaction[3] or using other reagents.[4]
- CH3CO2H + Br2 → CH2BrCO2H + HBr
See also
References
- ↑ Dippy, J. F. J., Hughes, S. R. C., Rozanski, A., J. Chem Soc., 1959, 2492.
- ↑ "Bromoacetic acid" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/6227#section=GHS-Classification.
- ↑ Dagani, M. J.; Barda, H. J.; Benya, T. J.; Sanders, D. C.. "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a04_405.
- ↑ Natelson, S.; Gottfried, S. (1955). "Ethyl Bromoacetate". Organic Syntheses. http://www.orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=cv3p0381.; Collective Volume, 3, pp. 381.
External links
 |