Chemistry:DBNPA
| |||
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
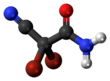
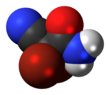
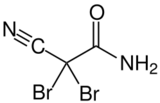
2,2-Dibromo-2-cyanoacetamide[1] | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
|Section1=! colspan=2 style="background: #f8eaba; text-align: center;" |Identifiers
|-
|
|
|-
|
|
|-
|
|-
|
- 233-539-7
|-
| MeSH
| 2,2-dibromo-3-nitrilopropionamide
|-
|
|
|- | RTECS number
|
- AB5956000
|- | UNII
|
|- | UN number | 1759 |-
| colspan="2" |
- InChI=1S/C3H2Br2N2O/c4-3(5,1-6)2(7)8/h(H2,7,8)
 Key: UUIVKBHZENILKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Key: UUIVKBHZENILKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|-
| colspan="2" |
- NC(=O)C(Br)(Br)C#N
|- |Section2=! colspan=2 style="background: #f8eaba; text-align: center;" |Properties
|-
|
| C3H2Br2N2O
|- | Molar mass
| 241.870 g·mol−1
|- | Appearance | White, translucent crystals |-
| Melting point
| 122 to 125 °C (252 to 257 °F; 395 to 398 K)
|- |Section3=! colspan=2 style="background: #f8eaba; text-align: center;" |Hazards
|-
| GHS pictograms
| 

 |-
| GHS Signal word
|DANGER
|-
| GHS Signal word
|DANGER
|-
|
| H314, H317, H400 |-
|
| P273, P280, P305+351+338, P310 |-
| colspan=2 style="text-align:left; background-color:#f1f1f1;" | Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC):
|-
|- style="background:#f4f4f4;"
| style="padding-left:1em;" |
| 10 mg kg−1 (intravenous, mouse)
|-
|- |Section4=! colspan=2 style="background: #f8eaba; text-align: center;" |Related compounds
|-
|
| Cyanoacetamide |- }}
DBNPA or 2,2-dibromo-3-nitrilopropionamide is a quick-kill biocide that easily hydrolyzes under both acidic and alkaline conditions. It is preferred for its instability in water as it quickly kills and then quickly degrades to form a number of products, depending on the conditions, including ammonia, bromide ions, dibromoacetonitrile, and dibromoacetic acid.[2] DBNPA acts similar to the typical halogen biocides.
DBNPA is used in a wide variety of applications. Some examples are in papermaking as a preservative in paper coating and slurries. It is also used as slime control on papermachines, and as a biocide in hydraulic fracturing wells and in cooling water.[2]
References
- ↑ "2,2-dibromo-3-nitrilopropionamide - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=25059. Retrieved 9 June 2012.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED) 2,2-dibromo-3-nitrilopropionamide (DBNPA)". "EPA 738-R-94-026". US EPA. September 1994. pp. 179. Archived from the original on 2014-10-16. https://web.archive.org/web/20141016103917/http://www.epa.gov/oppsrrd1/REDs/3056.pdf. Retrieved 2012-06-14.
 |