Constant-mean-curvature surface
In differential geometry, constant-mean-curvature (CMC) surfaces are surfaces with constant mean curvature.[1][2] This includes minimal surfaces as a subset, but typically they are treated as special case.
Note that these surfaces are generally different from constant Gaussian curvature surfaces, with the important exception of the sphere.
History
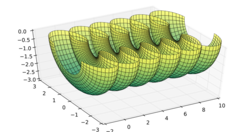
In 1841 Delaunay proved that the only surfaces of revolution with constant mean curvature were the surfaces obtained by rotating the roulettes of the conics. These are the plane, cylinder, sphere, the catenoid, the unduloid and nodoid.[3]
In 1853 J. H. Jellet showed that if [math]\displaystyle{ S }[/math] is a compact star-shaped surface in [math]\displaystyle{ \R^3 }[/math] with constant mean curvature, then it is the standard sphere.[4] Subsequently, A. D. Alexandrov proved that a compact embedded surface in [math]\displaystyle{ \R^3 }[/math] with constant mean curvature [math]\displaystyle{ H \neq 0 }[/math] must be a sphere.[5] Based on this H. Hopf conjectured in 1956 that any immersed compact orientable constant mean curvature hypersurface in [math]\displaystyle{ \R^n }[/math]must be a standard embedded [math]\displaystyle{ n-1 }[/math] sphere. This conjecture was disproven in 1982 by Wu-Yi Hsiang using a counterexample in [math]\displaystyle{ \R^4 }[/math]. In 1984 Henry C. Wente constructed the Wente torus, an immersion into [math]\displaystyle{ \R^3 }[/math] of a torus with constant mean curvature. [6]
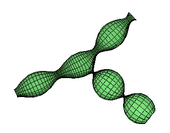
Up until this point it had seemed that CMC surfaces were rare; new techniques produced a plethora of examples.[7] In particular gluing methods appear to allow combining CMC surfaces fairly arbitrarily.[8][9] Delaunay surfaces can also be combined with immersed "bubbles", retaining their CMC properties.[10]
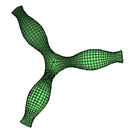
Meeks showed that there are no embedded CMC surfaces with just one end in [math]\displaystyle{ \R^3 }[/math].[11] Korevaar, Kusner and Solomon proved that a complete embedded CMC surface will have ends asymptotic to unduloids.[12] Each end carries a [math]\displaystyle{ n(2\pi-n) }[/math] "force" along the asymptotic axis of the unduloid (where n is the circumference of the necks), the sum of which must be balanced for the surface to exist. Current work involves classification of families of embedded CMC surfaces in terms of their moduli spaces.[13] In particular, for [math]\displaystyle{ k \geq 3 }[/math] coplanar k-unduloids of genus 0 satisfy [math]\displaystyle{ \sum_{i=1}^k n_i \leq (k-1)\pi }[/math] for odd k, and [math]\displaystyle{ \sum_{i=1}^k n_i \leq k\pi }[/math] for even k. At most k − 2 ends can be cylindrical.[7]
Generation methods
Representation formula
Like for minimal surfaces, there exist a close link to harmonic functions. An oriented surface [math]\displaystyle{ S }[/math] in [math]\displaystyle{ \R^3 }[/math] has constant mean curvature if and only if its Gauss map is a harmonic map.[14] Kenmotsu’s representation formula[15] is the counterpart to the Weierstrass–Enneper parameterization of minimal surfaces:
Let [math]\displaystyle{ V }[/math] be an open simply connected subset of [math]\displaystyle{ \C }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ H }[/math] be an arbitrary non-zero real constant. Suppose [math]\displaystyle{ \phi: V \rightarrow \C }[/math] is a harmonic function into the Riemann sphere. If [math]\displaystyle{ \phi_{\bar z} \neq 0 }[/math] then [math]\displaystyle{ X : V \rightarrow R }[/math] defined by
- [math]\displaystyle{ X(z) = \Re \int_{z_0}^z X_z(z')\,dz' }[/math]
with
- [math]\displaystyle{ X_z(z)=\frac{-1}{H(1+\phi(z)\bar\phi(z))^2} \left \{(1-\phi(z)^2, i(1+\phi(z)^2), 2\phi(z)) \frac{\bar{\partial\phi}}{\partial \bar z}(z) \right \} }[/math]
for [math]\displaystyle{ z \in V }[/math] is a regular surface having [math]\displaystyle{ \phi }[/math] as Gauss map and mean curvature [math]\displaystyle{ H }[/math].
For [math]\displaystyle{ \phi(z)=-1/\bar z }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ H=1 }[/math] this produces the sphere. [math]\displaystyle{ \phi(z)=-e^{ix} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ H=1/2 }[/math] gives a cylinder where [math]\displaystyle{ z=x+iv }[/math].
Conjugate cousin method
Lawson showed in 1970 that each CMC surface in [math]\displaystyle{ \R^3 }[/math]has an isometric "cousin" minimal surface in [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{S}^3 }[/math].[16][17] This allows constructions starting from geodesic polygons in [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{S}^3 }[/math], which are spanned by a minimal patch that can be extended into a complete surface by reflection, and then turned into a CMC surface.
CMC Tori
Hitchin, Pinkall, Sterling and Bobenko showed that all constant mean curvature immersions of a 2-torus into the space forms [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{R}^3, \mathbb{S}^3 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{H}^3 }[/math] can be described in purely algebro-geometric data. This can be extended to a subset of CMC immersions of the plane which are of finite type. More precisely there is an explicit bijection between CMC immersions of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{R}^2 }[/math] into [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{R}^3, \mathbb{S}^3 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{H}^3 }[/math], and spectral data of the form [math]\displaystyle{ (\Sigma, \lambda, \rho, \lambda_1, \lambda_2, L) }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \Sigma }[/math] is a hyperelliptic curve called the spectral curve, [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda }[/math] is a meromorphic function on [math]\displaystyle{ \Sigma }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda_1 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda_2 }[/math] are points on [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{C}\setminus\{0\} }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \rho }[/math] is an antiholomorphic involution and [math]\displaystyle{ L }[/math] is a line bundle on [math]\displaystyle{ \Sigma }[/math] obeying certain conditions.[18][19][20]
Discrete numerical methods
Discrete differential geometry can be used to produce approximations to CMC surfaces (or discrete counterparts), typically by minimizing a suitable energy functional.[21][22]
Applications
CMC surfaces are natural for representations of soap bubbles, since they have the curvature corresponding to a nonzero pressure difference.
Besides macroscopic bubble surfaces CMC surfaces are relevant for the shape of the gas–liquid interface on a superhydrophobic surface.[23]
Like triply periodic minimal surfaces there has been interest in periodic CMC surfaces as models for block copolymers where the different components have a nonzero interfacial energy or tension. CMC analogs to the periodic minimal surfaces have been constructed, producing unequal partitions of space.[24][25] CMC structures have been observed in ABC triblock copolymers.[26]
In architecture CMC surfaces are relevant for air-supported structures such as inflatable domes and enclosures, as well as a source of flowing organic shapes.[27]
See also
References
- ↑ Nick Korevaar, Jesse Ratzkin, Nat Smale, Andrejs Treibergs, A survey of the classical theory of constant mean curvature surfaces in R3, 2002 [1]
- ↑ Carl Johan Lejdfors, Surfaces of Constant Mean Curvature. Master’s thesis Lund University, Centre for Mathematical Sciences Mathematics 2003:E11 [2]
- ↑ C. Delaunay, Sur la surface de révolution dont la courbure moyenne est constante, J. Math. Pures Appl., 6 (1841), 309–320.
- ↑ J. H. Jellet, Sur la Surface dont la Courbure Moyenne est Constant, J. Math. Pures Appl., 18 (1853), 163–167
- ↑ A. D. Alexandrov, Uniqueness theorem for surfaces in the large, V. Vestnik, Leningrad Univ. 13, 19 (1958), 5–8, Amer. Math. Soc. Trans. (Series 2) 21, 412–416.
- ↑ Wente, Henry C. (1986), "Counterexample to a conjecture of H. Hopf.", Pacific Journal of Mathematics 121: 193–243, doi:10.2140/pjm.1986.121.193, http://projecteuclid.org/euclid.pjm/1102702809.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Karsten Grosse-Brauckmann, Robert B. Kusner, John M. Sullivan. Coplanar constant mean curvature surfaces. Comm. Anal. Geom. 15:5 (2008) pp. 985–1023. ArXiv math.DG/0509210. [3]
- ↑ N. Kapouleas. Complete constant mean curvature surfaces in Euclidean three space, Ann. of. Math. (2) 131 (1990), 239–330
- ↑ Rafe Mazzeo, Daniel Pollack, Gluing and Moduli for Noncompact Geometric Problems. 1996 arXiv:dg-ga/9601008 [4]
- ↑ I. Sterling and H. C. Wente, Existence and classification of constant mean curvature multibubbletons of finite and infinite type, Indiana Univ. Math. J. 42 (1993), no. 4, 1239–1266.
- ↑ Meeks W. H., The topology and geometry of embedded surfaces of constant mean curvature, J. Diff. Geom. 27 (1988) 539–552.
- ↑ Korevaar N., Kusner R., Solomon B., The structure of complete embedded surfaces with constant mean curvature, J. Diff. Geom. 30 (1989) 465–503.
- ↑ John M. Sullivan, A Complete Family of CMC Surfaces. In Integrable Systems, Geometry and Visualization, 2005, pp 237–245. [5]
- ↑ Shoichi Fujimori, Shimpei Kobayashi and Wayne Rossman, Loop Group Methods for Constant Mean Curvature Surfaces. Rokko Lectures in Mathematics 2005 arXiv:math/0602570
- ↑ K. Kenmotsu, Weierstrass Formula for Surfaces of Prescribed Mean Curvature, Math. Ann., 245 (1979), 89–99
- ↑ Lawson H.B., “Complete minimal surfaces in S3”, Annals of Mathematics 92 (1970) 335–374.
- ↑ Karsten Grosse-Brauckmann, Robert B Kusner, John M Sullivan. Triunduloids: Embedded constant mean curvature surfaces with three ends and genus zero. J. Reine Angew. Math., 564, pp. 35–61 2001 arXiv:math/0102183v2 [6]
- ↑ Hitchin, Nigel (1990). "Harmonic maps from a 2-torus to the 3-sphere". Journal of Differential Geometry 31 (3): 627–710. doi:10.4310/jdg/1214444631.
- ↑ Pinkall, U.; Sterling, I. (1989). "On the classification of constant mean curvature tori". Annals of Mathematics. Second 130 (2): 407–451. doi:10.2307/1971425.
- ↑ Bobenko, A. I. (1991). "Surfaces of constant mean curvature and integrable equations". Russian Math. Surveys 46 (4): 1–45. doi:10.1070/RM1991v046n04ABEH002826. http://www.mathnet.ru/php/archive.phtml?wshow=paper&jrnid=rm&paperid=4628&option_lang=eng.
- ↑ Smith, J. 2003. Three Applications of Optimization in Computer Graphics. PhD thesis, Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA [7]
- ↑ Hao Pan, Yi-King Choi, Yang Liu, Wenchao Hu, Qiang Du, Konrad Polthier, Caiming Zhang, Wenping Wang, Robust modeling of constant mean curvature surfaces. ACM Transactions on Graphics – SIGGRAPH 2012 Conference Proceedings. Volume 31 Issue 4, July 2012 Article No. 85
- ↑ E.J. Lobaton, T.R. Salamon. Computation of constant mean curvature surfaces: Application to the gas–liquid interface of a pressurized fluid on a superhydrophobic surface. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. Volume 314, Issue 1, 1 October 2007, Pages 184–198
- ↑ D. M. Anderson, H. T. Davis, L. E. Scriven, J. C. C. Nitsche, Periodic Surfaces of Prescribed Mean Curvature in Advances in Chemical Physics vol 77, eds. I. Prigogine and S. A. Rice, John Wiley & Sons, 2007 , p. 337–396
- ↑ Meinhard Wohlgemuth; Nataliya Yufa; James Hoffman; Edwin L. Thomas (2001). "Triply Periodic Bicontinuous Cubic Microdomain Morphologies by Symmetries". Macromolecules 34 (17): 6083–6089. doi:10.1021/ma0019499. Bibcode: 2001MaMol..34.6083W. https://secure.msri.org/about/sgp/jim/papers/morphbysymmetry/text/levelset.pdf.
- ↑ Samuel P. Gido , Dwight W. Schwark , Edwin L. Thomas , Maria do Carmo Goncalves, Observation of a non-constant mean curvature interface in an ABC triblock copolymer, Macromolecules, 1993, 26 (10), pp 2636–2640
- ↑ Helmut Pottmann, Yang Liu, Johannes Wallner, Alexander Bobenko, Wenping Wang. Geometry of Multi-layer Freeform Structures for Architecture. ACM Transactions on Graphics – Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 2007 Volume 26 Issue 3, July 2007 Article No. 65 [8]
External links
- CMC surfaces at the Scientific Graphics Project [9]
- GeometrieWerkstatt surface gallery [10]
- GANG gallery of CMC surfaces [11]
- Noid, software for computing n-noid CMC surfaces [12]
 |