Biology:Black-and-white antbird
| Black-and-white antbird | |
|---|---|

| |
| A male at Marchantaria island, Iranduba, Amazonas state, Brazil | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Thamnophilidae |
| Genus: | Myrmochanes Allen, 1889 |
| Species: | M. hemileucus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Myrmochanes hemileucus (Sclater, PL & Salvin, 1866)
| |
| |
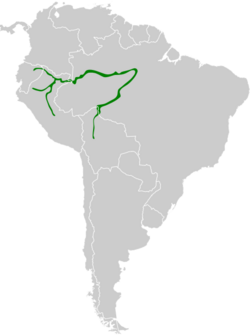
The black-and-white antbird (Myrmochanes hemileucus) is a species of bird in the family Thamnophilidae. It is monotypic within the genus Myrmochanes.[2] It is found in Bolivia, Brazil , Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests and subtropical or tropical moist shrubland.[1]
The black-and-white antbird was first described by the English ornithologists Philip Sclater and Osbert Salvin in 1866 and given the binomial name Hypocmenis hemileucus.[3]
Taxonomy and systematics
The black-and-white antbird (Myrmochanes hemileucus) is a species of bird in the family Thamnophilidae. It is monotypic within the genus Myrmochanes.[2]
While it has no other species in its genus, it is included in the tribe Formicivorini along with three other genera: Formicivora, Myrmotherula, and Terenura.[4]
The genus Myrmochanes was first described by the American ornithologist, Joel Asaph Allen in 1889.[5]
Description
Black-and-white antbirds are typically 11.5 cm in length[6] and weigh between 11 and 13 grams.[7] The males are black on top as well as the area from the base of the jaw and under the eyes to the auriculars. They have a white spot between their scapular feathers, which is almost always hidden, and their upper wing covert feathers are speckled with white. While their undersides are almost completely white, they have a bit of yellowish-brown on their flanks and bellies. Their short, graduated tail feathers have white tips, and their lower wing covert feathers are snow-white. The females are similar to the males, but with noticeable white markings on their lores. They also have more yellowish-brown around their rear undersides. The black-and-white antbird's beak is long, black, and slender. They have gray legs and brown irises.[7]
Distribution and habitat
The black-and-white antbirds are a species restricted to western Amazonia along the Amazon, Napo, and Ucayali rivers.[8] It is found in Bolivia, Brazil , Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. The black-and-white antbirds are primarily understory species. They are largely restricted to vine tangles where they occasionally ascend along tree trunks to the middle story.[8] They are habitat specialists but can no longer be considered river-island obligates, as they colonize appropriate habitat where it occurs on the mainland. On more mainland areas, it avoids natural habitats and prefers agricultural habitats.[9]
The vegetations most frequently visited by these antbirds are Tessaria thickets, young willows, wildcane,[6] and the underbrush of Cecropia trees, especially in tangles of bindweed.[7]
Behaviour and ecology
Feeding
The diet of the black-and-white antbirds consists of arthropods and small vertebrae. They have a very novel foraging strategy: army-ant-following. This occurs when birds prey upon arthropods and small vertebrates flushed from the forest floor by swarm raids of the army-ant Eciton burchellii. This specialization is most developed in the typical antbirds (Thamnophilidae) which are divisible into three specialization categories: (1) those that forage at swarms opportunistically as army-ants move through their territories (occasional followers), (2) those that follow swarms beyond their territories but also forage independently of swarms (regular followers), and (3) those that appear incapable of foraging independently of swarms (obligate followers).[10]
Status
According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN), the Black-and-white antbird is of least concern. However, they were predicted to have lost at least 50% of their habitat within Brazil due to effects of infrastructure development.[11]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 BirdLife International (2016). "Myrmochanes hemileucus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T22701743A93847249. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22701743A93847249.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22701743/93847249. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "ITIS Report: Myrmochanes". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=557934.
- ↑ Sclater, Philip L.; Salvin, Osbert (1866). "Catalogue of birds collected by Mr. E. Bartlett on the River Ucayali, Eastern Peru, with Notes and descriptions of new species". Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London (2): 175–201 [186–187]. https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/28627646.
- ↑ Ohlson, Jan I.; Irestedt, Martin; Ericson, Per G. P.; Fjeldså, Jon (2013-02-07). "Phylogeny and classification of the New World suboscines (Aves, Passeriformes)". Zootaxa 3613 (1): 1–35. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3613.1.1. ISSN 1175-5334. PMID 24698900. https://biotaxa.org/Zootaxa/article/view/zootaxa.3613.1.1.
- ↑ Allen, J.A. (1889). "List of the Birds Collected in Bolivia by Dr. H. H. Rusby, with Field Notes by the Collectors". Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 2: 77–112. http://digitallibrary.amnh.org/bitstream/handle/2246/1649//v2/dspace/ingest/pdfSource/bul/B002a07.pdf?sequence=1.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Ridgely, Robert; Tudor, Guy (2009). Field Guide to the Songbirds of South America: the Passerines (1 ed.). Austin: University of Texas Press. pp. 362. ISBN 978-0-292-71748-0.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Schulenberg, Thomas S.; Rosenberg, Gary H. (2011-06-30). "Black-and-white Antbird (Myrmochanes hemileucus)". Neotropical Birds. doi:10.2173/nb.bawant1.01. http://dx.doi.org/10.2173/nb.bawant1.01.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Rosenberg, Garry H. (1990). "Habitat Specialization and Foraging Behavior by Birds of Amazonian River Islands in Northeastern Peru". The Condor 92 (92): 427–443. doi:10.2307/1368240.
- ↑ Armacost Jr., J.W.; Capparella, Angelo P. (2012). “USE OF MAINLAND HABITATS BY SUPPOSED RIVER-ISLAND OBLIGATE BIRDS ALONG THE AMAZON RIVER IN PERU.” The Cooper Ornithological Society 114(1):56–61.
- ↑ Brumfield, R.T.; Tello, J.G.; Cheviron, Z.A.; Carling, M.D.; Crochet, N; Rosenberg, K.V. (2007). "Phylogenetic conservatism and antiquity of a tropical specialization: army-ant-following in the typical antbirds (Thamnophilidae)". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 45 (45): 1–13. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2007.07.019. PMID 17768072. https://digitalcommons.lsu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1583&context=biosci_pubs.
- ↑ Vale, M.M.; Cohn-Haft, M.A.R.I.O.; Bergen, S.; Pimm, S.L. (2008). "Effects of future infrastructure development on threat status and occurrence of Amazonian birds". Conservation Biology 22 (4): 1–13. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1739.2008.00939.x. PMID 18544091.
Wikidata ☰ Q1084883 entry
 |


