Biology:Peters's squirrel
| Peters's squirrel | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Rodentia |
| Family: | Sciuridae |
| Genus: | Sciurus |
| Species: | S. oculatus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Sciurus oculatus Peters, 1863
| |
| Subspecies[2] | |
| |
| |
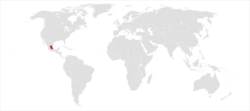
| Peters's squirrel's range | |
Peters's squirrel (Sciurus oculatus) is a tree squirrel in the genus Sciurus endemic to Mexico. It was first described by the German naturalist and explorer Wilhelm Peters in 1863. Three subspecies are recognised. It is a common species, and the IUCN has rated its conservation status as being of "least concern".
Description
Peters's squirrel is a large, mainly arboreal squirrel. The head-and-body length is 508 to 560 mm (20 to 22 in) with a tail of about 260 mm (10 in), and a weight of around 550 to 750 g (19 to 26 oz). The colouring varies somewhat between the subspecies but it is generally grey dorsally, the hairs having dark brown or black bases, and white or cream ventrally. The upper part of the tail is blackish while the underside is dark with white tips to the hairs. There is a pale ring of skin around the eyes, and an important identifying feature is the dentition, with one fewer upper premolars than other related species.[3]
Distribution and habitat
This squirrel is endemic to Mexico where it is found in the provinces of Guanajuato, Hidalgo, México State, Puebla, Querétaro, San Luis Potosí and Veracruz. It inhabits pine and oak forests, at altitudes between about 1,500 and 3,600 m (4,900 and 11,800 ft). It is also found on arid mountainsides and in valleys with arroyos.[1]
Ecology
The species is diurnal and usually lives a solitary life. During the summer these squirrels are frequently sighted, but not during the winter. The diet mainly consists of acorns and the seeds of pines, but other fruits and seeds are also eaten including wild figs and plums. The mating season seems to take place in summer and at this time, up to twenty individuals may accumulate in one tree, but little is known of their breeding behaviour. In parts of their range, they come into contact with the Mexican gray squirrel (Sciurus aureogaster) and the southern flying squirrel (Glaucomys volans).[3]
Status
Peters's squirrel has a wide range and is commonly seen in summer. No particular threats have been identified and it is present in a number of protected areas, so the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated its conservation status as being of "least concern".[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Álvarez-Castañeda, S.T.; Castro-Arellano, I.; Lacher, T.; Vázquez, E. (2016). "Sciurus oculatus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T20017A22246721. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T20017A22246721.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/20017/22246721. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ Thorington, R.W., Jr.; Hoffman, R.S. (2005). "Sciurus (Sciurus) oculatus". in Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 762–763. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494. http://www.departments.bucknell.edu/biology/resources/msw3/browse.asp?id=12400187.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Ceballos, Gerardo (2014). Mammals of Mexico. JHU Press. pp. 183–184. ISBN 978-1-4214-0843-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=UrvxBQAAQBAJ&pg=PA183.
Wikidata ☰ Q1770020 entry
 |


