Biology:Sambar deer
| Sambar | |
|---|---|

| |
| stag | |

| |
| female both R. u. unicolor in Kanha National Park, Madhya Pradesh, India | |
| Scientific classification Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Cervidae |
| Subfamily: | Cervinae |
| Genus: | Rusa |
| Species: | R. unicolor
|
| Binomial name | |
| Rusa unicolor (Kerr, 1792)
| |
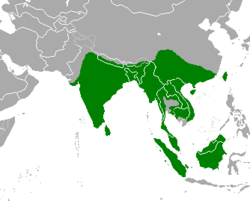
| |
| Range of the sambar deer | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The sambar (Rusa unicolor) is a large deer native to the Indian subcontinent, southern China, and Southeast Asia that is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List since 2008. Populations have declined substantially due to severe hunting, insurgency, and industrial exploitation of habitat.[1]
The name "sambar" is also sometimes used to refer to the Philippine deer, called the "Philippine sambar" and the Javan rusa, called the "Sunda sambar".
Description
The appearance and the size of sambar vary widely across their range, which has led to considerable taxonomic confusion in the past; over 40 different scientific synonyms have been used for the species. In general, they attain a height of 102 to 160 cm (40 to 63 in) at the shoulder and may weigh as much as 546 kg (1,204 lb), though more typically 100 to 350 kg (220 to 770 lb).[2][3] Head and body length varies from 1.62 to 2.7 m (5.3 to 8.9 ft), with a 22 to 35 cm (8.7 to 13.8 in) tail.[4] Individuals belonging to western subspecies tend to be larger than those from the east, and females are smaller than males.[5] Among all living cervid species, only the moose and the elk can attain larger sizes.[6]
The large, rugged antlers are typically rusine, the brow tines being simple and the beams forked at the tip, so they have only three tines. The antlers are typically up to 110 cm (43 in) long in fully adult individuals. As with most deer, only the males have antlers.[5]
The shaggy coat can be from yellowish brown to dark grey in colour, and while it is usually uniform in colour, some subspecies have chestnut marks on the rump and underparts. Sambar also have a small but dense mane, which tends to be more prominent in males. The tail is relatively long for deer, and is generally black above with a whitish underside.[5]
Adult males and pregnant or lactating females possess an unusual hairless, blood-red spot located about halfway down the underside of their throats. This sometimes oozes a white liquid, and is apparently glandular in nature.[7]
Distribution and habitat
The sambar is distributed in much of South Asia as far north as the south-facing slopes of the Himalayas in Nepal and India , in mainland Southeast Asia including Burma, Thailand, Indochina, the Malay Peninsula, South China including Hainan Island, Taiwan, and the Indonesian islands of Sumatra and Borneo. In the Himalayan foothills, Myanmar, and eastern Taiwan, it ranges up to 3,500 m (11,500 ft). It inhabits tropical dry forests, tropical seasonal forests, subtropical mixed forests with stands of conifers, broadleaved deciduous and broadleaved evergreen trees, to tropical rainforests, and seldom moves far from water sources.[1]
The sambar prefers the dense cover of deciduous shrubs and grasses,[7] although the exact nature of this varies enormously with the environment, because of its wide Asian range. Home range sizes are probably equally variable, but have been recorded as 1,500 ha (3,700 acres) for males and 300 ha (740 acres) for females in India.[5]
Ecology and behaviour
Sambar are nocturnal or crepuscular. The males live alone for much of the year, and the females live in small herds of up to 16 individuals. Indeed, in some areas, the average herd consists of only three or four individuals, typically consisting of an adult female, her most recent young, and perhaps a subordinate, immature female. This is an unusual pattern for deer, which more commonly live in larger groups. They often congregate near water, and are good swimmers.[5] Like most deer, sambar are generally quiet, although all adults can scream or make short, high-pitched sounds when alarmed. However, they more commonly communicate by scent marking and foot stamping.[citation needed]
Sambar feed on a wide variety of vegetation, including grasses, foliage, browse, fruit, and water plants, depending on the local habitat.[7] They also consume a great variety of shrubs and trees.[5]
Sambar have been seen congregating in large herds in protected areas such as national parks and reserves in India , Sri Lanka, and Thailand. In Taiwan, sambar along with sika deer, have been raised on farms for their antlers, which they drop annually in April to May and are highly prized for use as knife handles and as grips for handguns.[8]
Stags wallow and dig their antlers in urine-soaked soil, and then rub against tree trunks.[7] Sambar are capable of remarkable bipedalism for a deer species, and stags stand and mark tree branches above them with their antlers.[9] A stag also marks himself by spraying urine on his own face with a highly mobile penis.[7] Despite their lack of antlers, female sambar readily defend their young from most predators, which is relatively unusual among deer. When confronted by pack-hunting dholes or domestic dogs, a sambar lowers its head with an erect mane and lashes at the dogs. Sambar prefer to attack predators in shallow water. Several sambar may form a defensive formation, touching rumps and vocalising loudly at the dogs.[7] When sensing danger, a sambar stamps its feet and makes a ringing call known as "pooking" or "belling".[9]
They are favourite prey of tigers and Asiatic lions. In India, the sambar can comprise up to nearly 60% of the prey selected by the Bengal tiger.[10] Anecdotally, the tiger is said to even mimic the call of the sambar to deceive it while hunting.[10][11] They also can be taken by crocodiles, mostly the sympatric mugger crocodiles and estuarine crocodiles. Leopards and dholes largely prey on only young or sickly deer, though they can attack healthy adults, as well.[1]
Reproduction
Though they mate and reproduce year-round, sambar calving peaks seasonally. Oestrus lasts around 18 days. The male establishes a territory from which he attracts nearby females, but he does not establish a harem. The male stomps the ground, creating a bare patch, and often wallows in the mud, perhaps to accentuate the colour of his hair, which is typically darker than that of females. While they have been heard to make a loud, coarse bellow, rutting stags are generally not vocal.[5] Large, dominant stags defend nonexclusive territories surrounded by several smaller males,[9] with which they have bonded and formed alliances through sparring. When sparring with rival males, sambar lock antlers and push, like other deer, but uniquely, they also sometimes stand on their hind legs and clash downward into each other[7] in a manner similar to species of goat-antelope. Females also fight on their hind legs and use their fore legs to hit each other in the head.[5]
Courtship is based more on tending bonds rather than males vocally advertising themselves.[7] Females move widely among breeding territories seeking males to court.[5] When mounting, males do not clasp females. The front legs of the male hang loosely and intromission takes the form of a "copulatory jump".[7][9]
Gestation probably lasts around 8 months, although some studies suggest it may be slightly longer. Normally, only one calf is born at a time, although twins have been reported in up to 2% of births. Initially weighing 5 to 8 kg (11 to 18 lb), the calves are usually not spotted, although some subspecies have light spots which disappear not long after birth.[5] The young begin to take solid food at 5 to 14 days, and begin to ruminate after one month.[12] Sambar have lived up to 28 years in captivity, although they rarely survive more than 12 years in the wild.[5]
Taxonomy and evolution
Genetic analysis shows that the closest living relative of the sambar is probably the Javan rusa of Indonesia.[13] This is supported by reports that sambar can still interbreed to produce fertile hybrids with this species.[5]
Fossil sambar are known from the early Pleistocene, although they are very similar in form to early deer species from the Pliocene, with less of a resemblance to more modern cervines. The species probably arose in the tropical reaches of southern Asia, and later spread across its current range. Epirusa and Eucladoceros have both been proposed as possible ancestors of the living species and its closest relatives.[5]
Subspecies
The subspecies of sambar in India and Sri Lanka are the largest of the genus with the largest antlers both in size and in body proportions. The South China sambar of Southern China and mainland Southeast Asia is probably second in terms of size with slightly smaller antlers than the Indian sambar. The Sumatran sambar that inhabits the Malay Peninsula and Sumatra and the Bornean sambar seem to have the smallest antlers in proportion to their body size. The Formosan sambar is the smallest R. unicolor with antler-body proportions more similar to the South China sambar.
Currently, seven subspecies of sambar are recognised,[5][14] although many others have been proposed.
| Subspecies | Common name | Geographic range |
|---|---|---|
| R. u. boninensis[15] | Bonin sambar deer | Bonin Islands (extinct) |
| R. u. brookei | Borneo | |
R. u. cambojensis
|
Mainland Southeast Asia | |
| R. u. dejeani | South China sambar deer | Southern and southwestern China |
R. u. equina
|
Malayan sambar deer | Sumatra |
| R. u. hainana | Hainan sambar deer | Hainan, China |
R. u. swinhoii
|
Formosan sambar deer | Taiwan |
R. u. unicolor
|
Sri Lankan sambar deer | India, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka |
Introduced animal
Sambar deer have been introduced to various parts of the world including Australia , New Zealand, and the United States .[16]
Australia
In Australia, hunting sambar is a popular sport. Australian hunting fraternities prize large sambar trophies.[17] Excessive numbers of sambar deer affect native plants, threatening some species with extinction.
Sambar were introduced into Victoria at Mount Sugarloaf in the 1860s, in what is now Kinglake National Park, and at Harewood Estate near Tooradin.[18] They quickly adapted to the Koo-Wee-Rup Swamp and thereafter spread into the high country, where in 2017, numbers were estimated at between 750,000 and one million animals.[19] Later releases were at Ercildoune Estate near Ballarat, Wilsons Promontory, and French Island in Western Port. Another release occurred on the Cobourg Peninsula in the Northern Territory.[20] They are now found throughout Australia's northern and eastern coasts, in the states of Victoria, South Australia, Queensland, the Northern Territory, and the Australian Capital Territory.
In Victoria, sambar deer have been listed as a threat to biodiversity under the Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act 1988 because they reduce the number of native plant species.[21] The animals feed on some rare and endangered plants. More than 60 plant species have been identified as directly or indirectly threatened by sambar within Victoria.
Adult male sambar deer can significantly damage plants, removing most branches on some shrubs and sometimes girdling trees by thrashing their antlers on shrubs and sapling trees. They also feed on seedlings, fruit, or seeds of many plants. They leave territorial marks to advertise their territory.[22]
The spread of sambar has been steady in both NSW and Victoria, with animals being seen on many southern Victorian beaches since 1980, and as far east as Western Port and the outer suburbs of Melbourne.
Considerable debate exists about how they should be managed. Conservation groups believe their environmental effect outweighs their social value. Hunting organisations disagree and want to preserve deer populations for future generations. Sambar deer are protected wildlife game species in Victoria and New South Wales, and a game licence is required to hunt them. In Victoria, recent provisions have been made for landowners to control problem deer without having to obtain a Game Licence or Authority to Control Wildlife permit[23]. This allows a landowner or other authorised persons to remove problem deer within private property at any time and with no bag limits. They are declared pest species in all other Australian states and territories and can be hunted at any time with no bag limits. Environmental and conservation groups want them declared a feral species in all states, due to their exploding populations and the harm to biodiversity and native species.
In 2008/2009, 35,000 sambar were removed from public land in Victoria, many from national parks, by amateur hunters. This is a small fraction of the 40% of individuals in a sambar population that need to be removed to stop population growth.[24]
New Zealand
In New Zealand, sambar deer roam the coast and gullies in Horowhenua District, Manawatu District, Rangitikei, and Whanganui. Until recently, they were protected, but the Department of Conservation has now removed hunting regulations surrounding them, allowing them now to be hunted year round.[25]
United States
Sambar deer were introduced onto St. Vincent Island, Florida, in 1908[26] and increased to about 50 individuals by the 1950s. White-tailed deer also live on St. Vincent Island; however, they inhabit the highlands while the sambar deer mostly live in the lowlands and marshes. To ensure that the sambar deer population does not disrupt the native whitetails, hunting permits have been issued since 1987 to regulate the population. Each year, about 130 permits are offered for the three-day hunt. This maintains a sambar deer population of 70–100 individuals.[27] They do not herd, but occur in groups of four or five animals, possible family groups. Little is known about the sambar deer in Florida.[28]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Timmins, R.J.; Kawanishi, K.; Giman, B.; Lynam, A.J.; Chan, B.; Steinmetz, R.; Sagar Baral, H.; Samba Kumar, N. (2015). "Rusa unicolor". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species (IUCN) 2015: e.T41790A85628124. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T41790A22156247.en. http://www.iucnredlist.org/details/41790/0. Retrieved 15 January 2018.
- ↑ Burnie D and Wilson DE (Eds.), Animal: The Definitive Visual Guide to the World's Wildlife. DK Adult (2005), ISBN:0789477645
- ↑ "Comparative Placentation". Placentation.ucsd.edu. http://placentation.ucsd.edu/sdeer.html. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ↑ Boitani, Luigi (1984) Simon & Schuster's Guide to Mammals. Simon & Schuster/Touchstone Books, ISBN:978-0-671-42805-1
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 5.11 5.12 5.13 Leslie, D.M. (2011). "Rusa unicolor (Artiodactyla: Cervidae)". Mammalian Species 43 (1): 1–30. doi:10.1644/871.1.
- ↑ "Deer – Department of Primary Industries". Dpi.vic.gov.au. 3 January 2012. http://www.dpi.vic.gov.au/game-hunting/game/deer. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 7.8 Geist, V. (1998). Deer of the world: their evolution, behaviour, and ecology. Mechanicsburg: Stackpole Books. pp. 73–77.
- ↑ "Handle Materials". The Knife Connection. Archived from the original on 5 March 2012. https://web.archive.org/web/20120305115756/http://www.the-knife-connection.com/handle-materials--india-sambar-stag.html. Retrieved 11 March 2012.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 Schaller, G. (1967). The Deer and the Tiger: A Study of Wildlife in India. Chicago: University Of Chicago Press. pp. 134–148.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Ramesh, T.; Snehalatha, V.; Sankar, K.; Qureshi, Q. (2009). "Food habits and prey selection of tiger and leopard in Mudumalai Tiger Reserve, Tamil Nadu, India". Journal of Scientific Transactions in Environment and Technovation 2 (3): 170–181. http://oldwww.wii.gov.in/publications/researchpapers/2009/2009_Ramesh_food%20habits.pdf.
- ↑ Perry, R. (1965). The World of the Tiger. p. 260. ASIN: B0007DU2IU
- ↑ Semiadi, G. (1993). "Growth, milk intake, and behaviour of artificially reared sambar deer (Cervus unicolor) and red deer (Cervus elaphus)". Journal of Agricultural Science 121 (2): 273–281. doi:10.1017/S0021859600077157. http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=4819680&fulltextType=RA&fileId=S0021859600077157.
- ↑ Emerson, B.C.; Tate M.L. (1993). "Genetic analysis of evolutionary relationships among deer (subfamily Cervinae)". Journal of Heredity 84 (4): 266–273. PMID 8340615. http://jhered.oxfordjournals.org/content/84/4/266.abstract.
- ↑ Grubb, P. (2005). "Rusa unicolor". in Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 670–671. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494. http://www.departments.bucknell.edu/biology/resources/msw3/browse.asp?id=14200453.
- ↑ Pocock, R.I. (1943). "The Skull-characters of some of the Forms of Sambar (Rusa) occurring to the East of the Bay of Bengal. — Part III. Rusa nigricans and Rusa boninensis". Annals and Magazine of Natural History 10 (63): 191–196. doi:10.1080/03745481.1943.9728010. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/03745481.1943.9728010?journalCode=tnah17#.Vb3H3W6qqko.
- ↑ Long, J.L. (2003). Introduced Mammals of the World: Their History, Distribution and Influence. Clayton: CSIRO Publishing. ISBN:9780851997483
- ↑ Pearce, Ken (1992). Walking Them Up. Melbourne: Australian Deer Research Foundation. pp. xi–xv. ISBN 095934389X.
- ↑ "Sambar Deer (Rusa unicolor)". Australian Deer Association. 2017. http://www.austdeer.com.au/deer-in-australia/sambar-deer-rusa-unicolor/.
- ↑ Cattermole, Tony (31 Mar 2015). "Deer hunters work to control sambar deer numbers in Victoria's Alpine National Park". ABC News (Goulburn Murray). http://www.abc.net.au/news/2017-03-31/deer-hunters-cull-sambar-deer-in-alpine-national-park/8396774.
- ↑ Bentley, Arthur (1978). An introduction to the deer of Australia, with special reference to Victoria. Melbourne: Ray Manning for the Koetong Trust, Service Fund, Forests Commission, Victoria. pp. 32–37. ISBN 0724116893.
- ↑ "Flora and Fauna Guarantee Act 1988 Processes List". State Government of Victoria. December 2016. http://www.delwp.vic.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0005/364595/201612-FFG-Processes-list.pdf.
- ↑ OpenDocument Media Release: New Plan Needed To Manage Impact Of Sambar Deer. Minister for Environment & Climate Change (28 November 2007)
- ↑ Control of deer on private property
- ↑ Hone, J.; Duncan, R. P.; Forsyth, D. M. (2010). "Estimates of maximum annual population growth rates (rm) of mammals and their application in wildlife management". Journal of Applied Ecology 47 (3): 507–514. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2664.2010.01812.x.
- ↑ Deer: DOC's work. Department of Conservation (date=20 November 2013)
- ↑ "Sambar Deer – Cervus unicolor". Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission. http://myfwc.com/wildlifehabitats/nonnatives/mammals/sambar-deer/.
- ↑ Henry Cabbage (May–June 2006). "Going after 600-pound sambar deer in Florida!". Florida Wildlife Magazine: 39–41. Archived from the original on 20 March 2009. https://web.archive.org/web/20090320004004/http://floridawildlifemagazine.com/pdfs/may06sambardeer.pdf.
- ↑ Field Guide to Mammals. 2002. ISBN:0-679-44631-1.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
Wikidata ☰ Q229337 entry







