Chemistry:Aerobactin
From HandWiki
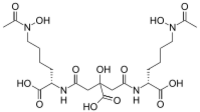
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(8S,16S)-3,12,21-Trihydroxy-2,10,14,22-tetraoxo-3,9,15,21-tetraazatricosane-8,12,16-tricarboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H36N4O13 | |
| Molar mass | 564.545 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Aerobactin is a bacterial iron chelating agent (siderophore)[1] found in E. coli.[2] It is a virulence factor enabling E. coli to sequester iron in iron-poor environments such as the urinary tract.[3]
Aerobactin is biosynthesized by the oxidation of lysine, catalyzed by the enzyme aerobactin synthase, which is then coupled to citric acid. The gene for this enzyme is found in the aerobactin operon, which is roughly 8 kilobases long and contains 5 or more genes in total.[4]
Yersinia pestis contains genes relating to aerobactin, but they have been inactivated by a frameshift mutation, thus Y. pestis is no longer able to synthesize aerobactin.[5]
Other homologs
- Rhizobactin from Sinorhizobium[6]
- Alcaligin from Bordetella[6]
References
- ↑ J. B. Neilands (1995). "Siderophores: Structure and Function of Microbial Iron Transport Compounds". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (45): 26723–26726. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.45.26723. PMID 7592901.
- ↑ "Aerobactin and other virulence factor genes among strains of Escherichia coli causing urosepsis: association with patient characteristics". Infect. Immun. 56 (2): 405–12. February 1988. doi:10.1128/iai.56.2.405-412.1988. PMID 2892793.
- ↑ Meyrier A (1999). "Urinary Tract Infection". Atlas of diseases of the kidney. 2. Oxford: Blackwell Science. ISBN 0-632-04387-3. http://www.kidneyatlas.org/book2/adk2_07.pdf.
- ↑ "Aerobactin biosynthesis and transport genes of plasmid ColV-K30 in Escherichia coli K-12". J. Bacteriol. 165 (2): 570–8. February 1986. doi:10.1128/jb.165.2.570-578.1986. PMID 2935523.
- ↑ "Analysis of the aerobactin and ferric hydroxamate uptake systems of Yersinia pestis". Microbiology 153 (Pt 7): 2332–41. July 2007. doi:10.1099/mic.0.2006/004275-0. PMID 17600077.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Cianciotto NP (June 2007). "Iron acquisition by Legionella pneumophila". Biometals 20 (3–4): 323–31. doi:10.1007/s10534-006-9057-4. PMID 17180462.
 |

