Biology:Lined seedeater
| Lined seedeater | |
|---|---|

| |
| Male | |

| |
| Female | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Thraupidae |
| Genus: | Sporophila |
| Species: | S. lineola
|
| Binomial name | |
| Sporophila lineola | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Loxia lineola (protonym) | |
The lined seedeater (Sporophila lineola) is a species of bird in the family Thraupidae.
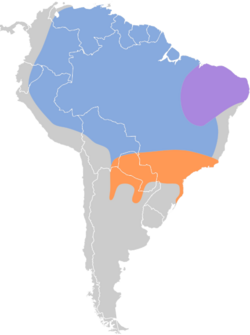
It is found in Argentina , Bolivia, Brazil , Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist shrubland, pastureland, and heavily degraded former forest.
Taxonomy
The lined seedeater was formally described by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the tenth edition of his Systema Naturae under the binomial name Loxia lineola.[2] Linnaeus mistakenly specified the "habitat" as Asia; the type locality was subsequently designated as the state of Bahia in Brazil.[3] The specific epithet lineola is Latin meaning "little line" (a diminutive of linea meaning "line").[4] The lined seedeater is now assigned to the genus Sporophila that was introduced by the German ornithologist Jean Cabanis in 1844.[5][6] The species is monotypic: no subspecies are recognised.[6]
Gallery
Male vocalization
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2018). "Sporophila lineola". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018: e.T22723434A132164395. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22723434A132164395.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22723434/132164395. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ↑ Linnaeus, Carl (1758) (in Latin). Systema Naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. 1 (10th ed.). Holmiae (Stockholm): Laurentii Salvii. p. 174. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/727081.
- ↑ Paynter, Raymond A. Jr, ed (1970). Check-List of Birds of the World. 13. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Museum of Comparative Zoology. p. 140. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/14483375.
- ↑ Jobling, James A. (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. p. 228. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- ↑ Cabanis, Jean (1844). "Avium conspectus quae in Republica Peruana reperiuntur et pleraeqiio observatae vel collectae sunt in itinere a Dr. J.J. de Tschudi" (in Latin). Archiv für Naturgeschichte 10: 262–317 [291]. https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/13704194.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Gill, Frank; Donsker, David; Rasmussen, Pamela, eds (July 2020). "Tanagers and allies". IOC World Bird List Version 10.2. International Ornithologists' Union. https://www.worldbirdnames.org/bow/tanagers/.
Further reading
- de Schauensee, Rodolphe Meyer (1952). "A review of the genus Sporophila". Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia 104: 175–181.
Wikidata ☰ Q1302765 entry
 |


