Biology:PASTA domain
| PASTA domain | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
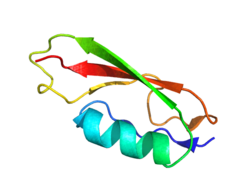 Cartoon representation of PASTA domain from Staphylococcus aureus. PDB entry 3m9g | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | PASTA | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF03793 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR005543 | ||||||||||
| SMART | PASTA | ||||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC51178 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1rp5 / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| CDD | cd06573 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
The PASTA domain is a small protein domain that can bind to the beta-lactam ring portion of various β-lactam antibiotics.[1] The domain was initially discovered in 2002 by Yeats and colleagues as a region of sequence similarity found in penicillin binding proteins and PknB-like kinases found in some bacteria. The name is an acronym derived from PBP and Serine/Threonine kinase Associated domain.
Structure
The PASTA domain adopts a structure composed of an alpha-helix followed by three beta strands. Recent structural studies show that the extracellular region of PknB (protein kinase B) that is composed of four PASTA domains shows a linear arrangement of the domains.[2]
Species distribution
PASTA domains are found in a variety of bacterial species including gram-positive Bacillota and Actinomycetota.
References
- ↑ "The PASTA domain: a beta-lactam-binding domain". Trends Biochem. Sci. 27 (9): 438–440. September 2002. doi:10.1016/s0968-0004(02)02164-3. PMID 12217513.
- ↑ "The structure of PknB extracellular PASTA domain from mycobacterium tuberculosis suggests a ligand-dependent kinase activation". Structure 18 (5): 606–15. May 2010. doi:10.1016/j.str.2010.02.013. PMID 20462494.
 |

