Biology:Sinaloa martin
| Sinaloa martin | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Hirundinidae |
| Genus: | Progne |
| Species: | P. sinaloae
|
| Binomial name | |
| Progne sinaloae Nelson, 1898
| |
| |
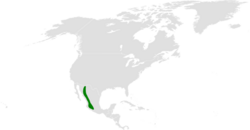
| Breeding distribution (winter distribution unknown) | |
The Sinaloa martin (Progne sinaloae) is a species of bird in the family Hirundinidae. This large and poorly-documented swallow is occasionally considered to be a subspecies of the Caribbean martin, Progne dominicensis.
It breeds semicolonially in sheer cliff faces within pine-oak forests of the Sierra Madre Occidental of western Mexico, nesting in cavities. Presumed migrant records also come from Belize and Guatemala. It is assumed to winter in South America; however, this is not known with certainty.[2]
Description
Adult males have dark iridescent blue-black feathers with a contrasting white patch covering the belly to the vent, much like the related Caribbean martin.[3] However, its reproductive situation and different habitat preference supports its status as a species.[4]
The adult female and immature form of the Sinaloa martin are very similar to related Progne species such as the Cuban martin, Caribbean martin, and purple martin.
Status
The range and status of this bird are generally poorly understood, and the species is considered to be rare. However, it has been shown that the Sinaloa martin continues to occupy its historical range. The lack of focus by both scientists and hobby birdwatchers has led to very little data being available to make meaningful population estimates, or to properly document population trends over time.[4]
Unlike what has been occurring with related species such as the purple martin and the Cuban martin,[5] competition for nesting sites with invasive European starlings (Sturnus vulgaris) and house sparrows (Passer domesticus) is not likely a significant risk to the Sinaloa martin's population as these invasive species have not become established in this species' breeding range.[4]
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2020). "Progne sinaloae". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020: e.T22712107A179699060. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22712107A179699060.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22712107/179699060. Retrieved 11 November 2021.
- ↑ "Progne sinaloae (Sinaloa Martin) - Avibase". https://avibase.bsc-eoc.org/species.jsp?avibaseid=0C028E2E4ADBF153.
- ↑ "Sinaloa Martin - eBird" (in en). https://ebird.org/species/sinmar1.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Lethaby, Nick (January 2010). "The current status of Sinaloa Martin Progne sinaloae". https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242693242.
- ↑ Kroenke, Steven (1999-11-11). "House Sparrow Revenge Syndrome". http://www.purplemartin.org/forumarchives/archive/HSrevenge.htm.
Wikidata ☰ Q2096782 entry
 |


