Biology:Olive woodpecker
| Olive woodpecker | |
|---|---|

| |
| D. g. subsp. persimilis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Piciformes |
| Family: | Picidae |
| Genus: | Dendropicos |
| Species: | D. griseocephalus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Dendropicos griseocephalus (Boddaert, 1783)
| |
| |
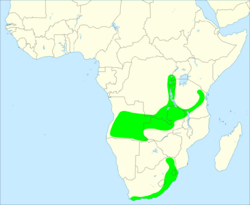
| Geographic distribution shown in green | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Chloropicus griseocephalus | |
The olive woodpecker (Dendropicos griseocephalus) is a species of bird in the woodpecker family Picidae.[2]
Taxonomy
The olive woodpecker was described by the French polymath Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon in 1780 in his Histoire Naturelle des Oiseaux from a specimen obtained from the Cape of Good Hope area of South Africa.[3] The bird was also illustrated in a hand-coloured plate engraved by François-Nicolas Martinet in the Planches Enluminées D'Histoire Naturelle which was produced under the supervision of Edme-Louis Daubenton to accompany Buffon's text.[4] Neither the plate caption nor Buffon's description included a scientific name but in 1783 the Dutch naturalist Pieter Boddaert coined the binomial name Picus griseocephalus in his catalogue of the Planches Enluminées.Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag
- D. g. ruwenzori (Sharpe, 1902) – Angola, north Zambia, north Malawi and central Tanzania to southeast DR Congo and southwest Uganda
- D. g. kilimensis (Neumann, 1926) – north and east Tanzania
- D. g. griseocephalus (Boddaert, 1783) – south Mozambique to South Africa
Distribution and habitat
The olive woodpecker is native to central, east and southern Africa, from the Ruwenzori Mountains to the Western Cape. It is found in Angola, Burundi, DRC, Eswatini, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, Rwanda, South Africa , Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. The species occupies a range of wooded and forested habitats from 450–3,700 m (1,480–12,140 ft).
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Dendropicos griseocephalus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T22681023A92889848. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22681023A92889848.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22681023/92889848. Retrieved 11 November 2021.
- ↑ Fuchs, J.; Pons, J. M. (2015). "A new classification of the pied woodpeckers assemblage (Dendropicini, Picidae) based on a comprehensive multi-locus phylogeny". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 88: 28–37. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2015.03.016. PMID 25818851.
- ↑ Buffon, Georges-Louis Leclerc de (1780). "Pie a tête gris du Cap de Bonne-Espérance" (in fr). Histoire Naturelle des Oiseaux. 13. Paris: De L'Imprimerie Royale. p. 38. https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/42410463.
- ↑ Buffon, Georges-Louis Leclerc de; Martinet, François-Nicolas; Daubenton, Edme-Louis; Daubenton, Louis-Jean-Marie (1765–1783). "Pie à tête gris, du Cap de Bonne-Esperance". Planches Enluminées D'Histoire Naturelle. 8. Paris: De L'Imprimerie Royale. Plate 786 Fig. 2. https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/35218467.
External links
- Olive woodpecker - Species text in The Atlas of Southern African Birds
- Xeno-canto: audio recordings of the olive woodpecker
Wikidata ☰ Q1263488 entry
 |


