Biology:Spectrin repeat
| Spectrin repeat | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
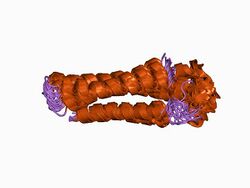 Structure of the spectrin repeat: a left-handed antiparallel triple-helical coiled-coil.[1] | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Spectrin | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00435 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR002017 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC50083 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1aj3 / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| CDD | cd00176 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Spectrin repeats[2] are found in several proteins involved in cytoskeletal structure. These include spectrin, alpha-actinin, dystrophin and more recently the plakin family. The spectrin repeat forms a three-helix bundle. These conform to the rules of the heptad repeat. Spectrin repeats give rise to linear proteins. This however may be due to sample bias in which linear and rigid structures are more amenable to crystallization. There are hints however, that some proteins harbouring spectrin repeats may also be flexible. This is most likely due to specifically evolved functional purposes.
Human proteins containing this domain
ACTN1; ACTN2; ACTN3; ACTN4; AKAP6; SYNE3; CATX-15; DMD; DRP2; DST; KALRN; MACF1; MCF2L; SPTA1; SPTAN1; SPTB; SPTBN1; SPTBN2; SPTBN4; SPTBN5; SYNE1; SYNE2; TRIO; UTRN;
References
- ↑ "Solution structure of the spectrin repeat: a left-handed antiparallel triple-helical coiled-coil". J. Mol. Biol. 273 (3): 740–51. October 1997. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1997.1344. PMID 9356261.
- ↑ "Crystal structure of the repetitive segments of spectrin". Science 262 (5142): 2027–2030. 1993. doi:10.1126/science.8266097. PMID 8266097.
- Jefferson, JJ; Ciatto, C; Shapiro, L; Liem, RK (2007). "Structural analysis of the plakin domain of bullous pemphigoid antigen1 (BPAG1) suggests that plakins are members of the spectrin superfamily.". Journal of Molecular Biology 366 (1): 244–57. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.11.036. PMID 17161423.
- Grum, VL; Li, D; MacDonald, RI; Mondragón, A (1999). "Structures of two repeats of spectrin suggest models of flexibility.". Cell 98 (4): 523–35. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81980-7. PMID 10481916.
Further reading
- "The spectrin repeat: a structural platform for cytoskeletal protein assemblies". FEBS Lett. 513 (1): 119–23. February 2002. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(01)03304-X. PMID 11911890.
- "Evolution of the spectrin repeat". BioEssays 19 (9): 811–7. September 1997. doi:10.1002/bies.950190911. PMID 9297972.
- Al-Jassar, C; Knowles, T; Jeeves, M; Kami, K; Behr, E; Bikker, H; Overduin, M; Chidgey, M (Jul 2, 2011). "The Nonlinear Structure of the Desmoplakin Plakin Domain and the Effects of Cardiomyopathy-Linked Mutations.". Journal of Molecular Biology 411 (5): 1049–61. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2011.06.047. PMID 21756917.
 |

