Chemistry:Fast Green FCF
| |
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
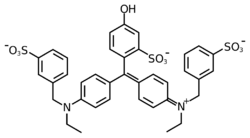
ethyl-[4-[[4-[ethyl-[(3-sulfophenyl)methyl]amino]phenyl]-(4-hydroxy-2-sulfophenyl)methylidene]-1-cyclohexa-2,5-dienylidene]-[(3-sulfophenyl)methyl]azanium
| |
| Other names
Food green 3,
FD&C Green No. 3, Green 1724, Solid Green FCF, and C.I. 42053 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C37H34N2Na2O10S3 | |
| Molar mass | 808.84 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards[1] | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P201, P202, P261, P264, P271, P280, P281, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P308+313, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Fast Green FCF, also called Food green 3, FD&C Green No. 3, Green 1724, Solid Green FCF, and C.I. 42053, is a turquoise triarylmethane food dye. Its E number is E143.
Fast Green FCF is recommended as a replacement of Light Green SF yellowish in Masson's trichrome, as its color is more brilliant and less likely to fade. It is used as a quantitative stain for histones at alkaline pH after acid extraction of DNA. It is also used as a protein stain in electrophoresis. Its absorption maximum is at 625 nm.
Fast Green FCF is poorly absorbed by the intestines.[2] Its use as a food dye is prohibited in the European Union and some other countries. It can be used for tinned green peas and other vegetables, jellies, sauces, fish, desserts, and dry bakery mixes at level of up to 100 mg/kg.[3] In the United States, Fast Green FCF is the least used of the seven main FDA approved dyes.
Toxicology
A reevaluation of Fast Green FCF published by the World Health Organization in 2017 concluded that it has low toxicity and is not carcinogenic or genotoxic, and that there were no health concerns with consumption of Fast Green FCF at the previously established allowable daily intake (which itself is much higher than estimates of actual dietary exposure to Fast Green FCF).[4]
Notes
- ↑ "Summary of Classification and Labelling". https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/4904.
- ↑ "Fast Green FCF". IPCS INchem. http://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v16je12.htm.
- ↑ "Fast Green FCF, INS: 143". Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations. http://www.fao.org/docrep/meeting/005/Y0474S/y0474s3b.htm.
- ↑ Evaluation of certain food additives: eighty-fourth report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. 2017. pp. 36–41. ISBN 9789241210164. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/259483/9789241210164-eng.pdf#page36. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
 |


