Biology:Porfiromycin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Promycin[1] |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
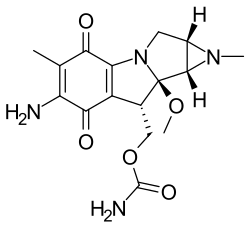
| Formula | C16H20N4O5 |
| Molar mass | 348.359 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Porfiromycin is an N-methyl derivative of the antineoplastic antibiotic, mitomycin C, which is isolated from various Streptomyces bacterial species.[2] As an antineoplastic agent, it is under investigation for the treatment of cancer, particularly head and neck cancer.[1]
Porfiromycin works by generating oxygen radicals and alkylating DNA, resulting in interstrand cross-links and single-strand breaks. This inhibits DNA synthesis and leads to the death of cancer cells. It has a higher toxicity towards hypoxic cells, making it an attractive option for cancer treatment.[2]
Porfiromycin can increase the risk of methemoglobinemia when taken with certain medications.[1] It belongs to the class of compounds known as mitomycins, which are characterized by their aziridine ring linked to a 7-amino-6-methyl-cyclohexa[b]pyrrolizine-5,8-dione structure.[1]
References
 |

