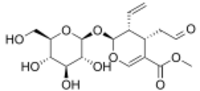
Chemistry:Secologanin
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Methyl (2S,3R,4S)-3-ethenyl-2-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-4-(2-oxoethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-5-carboxylate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Methyl (4S,5R,6S)-3-ethenyl-4-(2-oxoethyl)-2-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-5-carboxylate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H24O10 | |
| Molar mass | 388.369 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.42 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 595.5 °C (1,103.9 °F; 868.6 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Secologanin is a secoiridoid monoterpene synthesized from geranyl pyrophosphate in the mevalonate pathway. Secologanin then proceeds with dopamine or tryptamine to form ipecac and terpene indole alkaloids, respectively.
Biosynthesis
Secologanin biosynthesis begins from geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) taken from the mevalonate pathway used to make terpenoids. Recent efforts have characterized the entire secologanin biosynthetic pathway.[1] Secologanin is formed from loganin through the action of the enzyme secologanin synthase. Secologanin is then able to proceed onto produce ipecac and terpene indole alkaloids.[2]
References
- ↑ Miettinen, Karel; Dong, Lemeng; Navrot, Nicolas; Schneider, Thomas; Burlat, Vincent; Pollier, Jacob; Woittiez, Lotte; van der Krol, Sander et al. (7 April 2014). "The seco-iridoid pathway from Catharanthus roseus". Nature Communications 5 (1): 3606. doi:10.1038/ncomms4606. PMID 24710322.
- ↑ "Secologanin Biosynthesis". http://www.chem.qmul.ac.uk/iubmb/enzyme/reaction/terp/loganin.html. Retrieved 31 May 2011.
 |

