Chemistry:Aspalathin
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
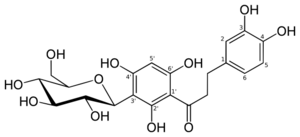
3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-1-[5-(β-D-glucopyranosyl)-2,4-dihydroxyphenyl]propan-1-one
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-1-{2,4-dihydroxy-5-[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]phenyl}propan-1-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H24O11 | |
| Molar mass | 452.412 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Aspalathin is a C-linked dihydrochalcone glucoside found in rooibos tea, a herbal tea prepared from the South African rooibos plant, Aspalathus linearis (Fabaceae).[1]
It was first isolated in 1965 by chromatography.[2]
It has demonstrated antidiabetic activity.[3]
References
- ↑ Bramati L (2002). "Quantitative Characterization of Flavonoid Compounds in Rooibos Tea (Aspalathus linearis) by LC-UV/DAD". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry (Elsevier) 50 (20): 5513–5519. doi:10.1021/jf025697h. PMID 12236672.
- ↑ Koeppen, B. H.; Roux, D. G. (June 1966). "C-Glycosylflavonoids. The chemistry of aspalathin". Biochemical Journal 99 (3): 604–609. doi:10.1042/bj0990604. ISSN 0264-6021. PMID 4290475.
- ↑ Bader, Michael; Mazibuko-Mbeje, Sithandiwe E.; Dludla, Phiwayinkosi V.; Johnson, Rabia; Joubert, Elizabeth; Louw, Johan; Ziqubu, Khanyisani; Tiano, Luca et al. (2019). "Aspalathin, a natural product with the potential to reverse hepatic insulin resistance by improving energy metabolism and mitochondrial respiration". PLOS ONE 14 (5): e0216172. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0216172. ISSN 1932-6203. PMID 31048842. Bibcode: 2019PLoSO..1416172M.
External links
 |

