Chemistry:Dihydrochalcone
From HandWiki
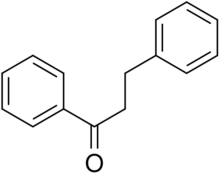
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3-Diphenylpropan-1-one | |
| Other names
Hydrochalcone
Benzylacetophenone Hydrocinnamophenone 3-Phenylpropiophenone Phenethyl phenyl ketone Phenyl phenethyl ketone β-Phenylpropiophenone 1,3-Diphenyl-1-propanone ω-Benzyl acetophenone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H14O | |
| Molar mass | 210.27 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.0614 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 72–75 °C (162–167 °F; 345–348 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dihydrochalcone (DHC) is the organic compound with the formula C6H5C(O)(CH2)2C6H5. It is the reduced derivative of chalcone (C6H5C(O)(CH)2C6H5). It is white solid that is soluble in many organic solvents. Dihydrochalcone per se is often minor significance, but some derivatives occur in nature and have attracted attention as drugs.[1]
Natural dihydrochalcones
- Aspalathin, a C-linked dihydrochalcone glucoside found in rooibos, a common herbal tea
- Naringin dihydrochalcone, an artificial sweetener derived from naringin
- Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone, an artificial sweetener derived from citrus
- Nothofagin, a C-linked phloretin glucoside found in rooibos
- Phloretin
- Isosalipurpurin
Dihydrochalcones (3′,5′-dihydroxy-2′,4′,6′-trimethoxydihydrochalcone (methyl linderone) and 2′-hydroxy-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetramethoxydihydrochalcone (dihydrokanakugiol) can be found in twigs of Lindera lucida.[2]
References
- ↑ Tomás-Barberán, Francisco A.; Clifford, Michael N. (2000). "Flavanones, Chalcones and Dihydrochalcones - Nature, Occurrence and Dietary Burden". Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 80 (7): 1073–1080. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0010(20000515)80:7<1073::AID-JSFA568>3.0.CO;2-B.
- ↑ A dihydrochalcone from Lindera lucida. Yuan-Wah Leong, Leslie J. Harrison, , Graham J. Bennett, Azizol A. Kadir and Joseph D. Connolly, Phytochemistry, Volume 47, Issue 5, March 1998, Pp. 891-894, doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(97)00947-3
 |
