Chemistry:Pachymic acid
From HandWiki
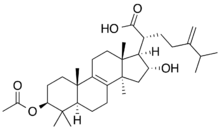
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3β-(Acetyloxy)-16α-hydroxy-24-methylidenelanost-8-en-21-oic acid
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R)-2-[(1R,2R,3aR,5aR,6S,9aS,11aR)-7-(Acetyloxy)-2-hydroxy-3a,6,6,9a,11a-pentamethyl-2,3,3a,4,5,5a,6,7,8,9,9a,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-1-yl]-6-methyl-5-methylideneheptanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C33H52O5 | |
| Molar mass | 528.76 g/mol |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 612.2±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 184.7±25.0 °C [citation needed] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Pachymic acid is a naturally occurring steroid that can be extracted from the parasitic fungus Wolfiporia extensa (synonym Wolfiporia cocos). The dried sclerotia of the fungus is used as a traditional Chinese medicine, and pachymic acid is thought to be the principal bioactive component of it.[1]
Effects
Pachymic acid is known to inhibit the Epstein–Barr virus and to inhibit the snake venom phospholipase A2.[2] It also has antitumor and anti-inflammatory properties.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Shu, Shaohua; Chen, Bei; Zhou, Mengchun; Zhao, Xinmei; Xia, Haiyang; Wang, Mo (2013). "De Novo Sequencing and Transcriptome Analysis of Wolfiporia cocos to Reveal Genes Related to Biosynthesis of Triterpenoids". PLOS ONE 8 (8): e71350. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0071350. PMID 23967197. Bibcode: 2013PLoSO...871350S.
- ↑ "Pachymic acid Biological Test Results". 3 March 2016. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Pachymic_acid#section=Biological-Test-Results.
 |

