Scherk surface
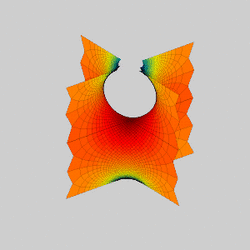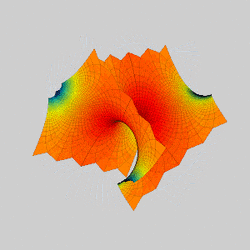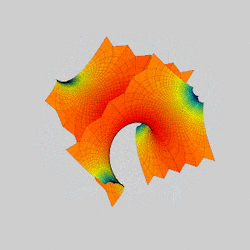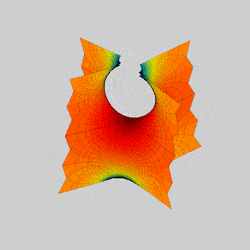
In mathematics, a Scherk surface (named after Heinrich Scherk) is an example of a minimal surface. Scherk described two complete embedded minimal surfaces in 1834;[1] his first surface is a doubly periodic surface, his second surface is singly periodic. They were the third non-trivial examples of minimal surfaces (the first two were the catenoid and helicoid).[2] The two surfaces are conjugates of each other.
Scherk surfaces arise in the study of certain limiting minimal surface problems and in the study of harmonic diffeomorphisms of hyperbolic space.
Scherk's first surface
Scherk's first surface is asymptotic to two infinite families of parallel planes, orthogonal to each other, that meet near z = 0 in a checkerboard pattern of bridging arches. It contains an infinite number of straight vertical lines.
Construction of a simple Scherk surface
File:Scherk-1 surface unit cell.stl
Consider the following minimal surface problem on a square in the Euclidean plane: for a natural number n, find a minimal surface Σn as the graph of some function
- [math]\displaystyle{ u_{n} : \left( - \frac{\pi}{2}, + \frac{\pi}{2} \right) \times \left( - \frac{\pi}{2}, + \frac{\pi}{2} \right) \to \mathbb{R} }[/math]
such that
- [math]\displaystyle{ \lim_{y \to \pm \pi / 2} u_{n} \left( x, y \right) = + n \text{ for } - \frac{\pi}{2} \lt x \lt + \frac{\pi}{2}, }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \lim_{x \to \pm \pi / 2} u_{n} \left( x, y \right) = - n \text{ for } - \frac{\pi}{2} \lt y \lt + \frac{\pi}{2}. }[/math]
That is, un satisfies the minimal surface equation
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathrm{div} \left( \frac{\nabla u_{n} (x, y)}{\sqrt{1 + | \nabla u_{n} (x, y) |^{2}}} \right) \equiv 0 }[/math]
and
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Sigma_{n} = \left\{ (x, y, u_{n}(x, y)) \in \mathbb{R}^{3} \left| - \frac{\pi}{2} \lt x, y \lt + \frac{\pi}{2} \right. \right\}. }[/math]
What, if anything, is the limiting surface as n tends to infinity? The answer was given by H. Scherk in 1834: the limiting surface Σ is the graph of
- [math]\displaystyle{ u : \left( - \frac{\pi}{2}, + \frac{\pi}{2} \right) \times \left( - \frac{\pi}{2}, + \frac{\pi}{2} \right) \to \mathbb{R}, }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ u(x, y) = \log \left( \frac{\cos (x)}{\cos (y)} \right). }[/math]
That is, the Scherk surface over the square is
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Sigma = \left\{ \left. \left(x, y, \log \left( \frac{\cos (x)}{\cos (y)} \right) \right) \in \mathbb{R}^{3} \right| - \frac{\pi}{2} \lt x, y \lt + \frac{\pi}{2} \right\}. }[/math]
More general Scherk surfaces
One can consider similar minimal surface problems on other quadrilaterals in the Euclidean plane. One can also consider the same problem on quadrilaterals in the hyperbolic plane. In 2006, Harold Rosenberg and Pascal Collin used hyperbolic Scherk surfaces to construct a harmonic diffeomorphism from the complex plane onto the hyperbolic plane (the unit disc with the hyperbolic metric), thereby disproving the Schoen–Yau conjecture.
Scherk's second surface
File:Scherk-2 surface unit cell.stl
Scherk's second surface looks globally like two orthogonal planes whose intersection consists of a sequence of tunnels in alternating directions. Its intersections with horizontal planes consists of alternating hyperbolas.
It has implicit equation:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \sin(z) - \sinh(x)\sinh(y)=0 }[/math]
It has the Weierstrass–Enneper parameterization [math]\displaystyle{ f(z) = \frac{4}{1-z^4} }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ g(z) = iz }[/math] and can be parametrized as:[3]
- [math]\displaystyle{ x(r,\theta) = 2 \Re ( \ln(1+re^{i \theta}) - \ln(1-re^{i \theta}) ) = \ln \left( \frac{1+r^2+2r \cos \theta}{1+r^2-2r \cos \theta} \right) }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ y(r,\theta) = \Re ( 4i \tan^{-1}(re^{i \theta})) = \ln \left( \frac{1+r^2-2r \sin\theta}{1+r^2+2r \sin \theta} \right) }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ z(r,\theta) = \Re ( 2i(-\ln(1-r^2e^{2i \theta}) + \ln(1+r^2e^{2i \theta}) ) = 2 \tan^{-1}\left( \frac{2 r^2 \sin 2\theta}{r^4-1} \right) }[/math]
for [math]\displaystyle{ \theta \in [0, 2\pi) }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ r \in (0,1) }[/math]. This gives one period of the surface, which can then be extended in the z-direction by symmetry.
The surface has been generalised by H. Karcher into the saddle tower family of periodic minimal surfaces.
Somewhat confusingly, this surface is occasionally called Scherk's fifth surface in the literature.[4][5] To minimize confusion it is useful to refer to it as Scherk's singly periodic surface or the Scherk-tower.
External links
- Hazewinkel, Michiel, ed. (2001), "Scherk surface", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer Science+Business Media B.V. / Kluwer Academic Publishers, ISBN 978-1-55608-010-4, https://www.encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=Main_Page
- Scherk's first surface in MSRI Geometry [2]
- Scherk's second surface in MSRI Geometry [3]
- Scherk's minimal surfaces in Mathworld [4]
References
- ↑ H.F. Scherk, Bemerkungen über die kleinste Fläche innerhalb gegebener Grenzen, Journal für die reine und angewandte Mathematik, Volume 13 (1835) pp. 185–208 [1]
- ↑ "Heinrich Scherk - Biography". http://www-history.mcs.st-andrews.ac.uk/Biographies/Scherk.html.
- ↑ Eric W. Weisstein, CRC Concise Encyclopedia of Mathematics, 2nd ed., CRC press 2002
- ↑ Nikolaos Kapuoleas, Constructions of minimal surfaces by glueing minimal immersions. In Global Theory of Minimal Surfaces: Proceedings of the Clay Mathematics Institute 2001 Summer School, Mathematical Sciences Research Institute, Berkeley, California, June 25-July 27, 2001 p. 499
- ↑ David Hoffman and William H. Meeks, Limits of minimal surfaces and Scherk's Fifth Surface, Archive for rational mechanics and analysis, Volume 111, Number 2 (1990)
 |




