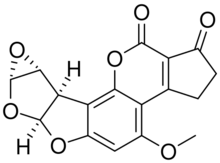
Chemistry:Aflatoxin B1 exo-8,9-epoxide
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(6aS,7aS,8aR,8bR)-4-Methoxy-2,3,6a,7a,8a,8b-hexahydrocyclopenta[c]oxireno[2′′,3′′:4′,5′]furo[3′,2′:4,5]furo[2,3-h][1]benzopyran-1,10-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H12O7 | |
| Molar mass | 328.276 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Aflatoxin B1 exo-8,9-epoxide is a toxic metabolite of aflatoxin B1. It's formed by the action of cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver.[1]
In the liver, aflatoxin B1 is metabolized to aflatoxin B1 exo-8,9-epoxide by the cytochrome P450 enzymes. The resulting epoxide can react with guanine in the DNA to cause DNA damage.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Arinç, Emel; Schenkman, John B.; Hodgson, Ernest (2012) (in en). Molecular and Applied Aspects of Oxidative Drug Metabolizing Enzymes. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 200. ISBN 9781461548553. https://books.google.com/books?id=1b0GCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA200.
- ↑ Turner, Paul Craig (2013). "The Molecular Epidemiology of Chronic Aflatoxin Driven Impaired Child Growth". Scientifica 2013: 152879. doi:10.1155/2013/152879. PMID 24455429.
 |

