Engineering:Dragline excavator

A dragline excavator is a piece of heavy equipment used in civil engineering and surface mining.
Draglines fall into two broad categories: those that are based on standard, lifting cranes, and the heavy units which have to be built on-site. Most crawler cranes, with an added winch drum on the front, can act as a dragline. These units (like other cranes) are designed to be dismantled and transported over the road on flatbed trailers. Draglines used in civil engineering are almost always of this smaller, crane type. These are used for road, port construction, pond and canal dredging, and as pile driving rigs. These types are built by crane manufacturers such as Link-Belt and Hyster.
The much larger type which is built on site is commonly used in strip-mining operations to remove overburden above coal and more recently for oil sands mining. The largest heavy draglines are among the largest mobile land machines ever built. The smallest and most common of the heavy type weigh around 8,000 tons while the largest built weighed around 13,000 tons.
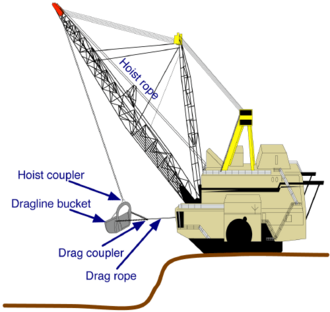
A dragline bucket system consists of a large bucket which is suspended from a boom (a large truss-like structure) with wire ropes. The bucket is maneuvered by means of a number of ropes and chains. The hoist rope, powered by large diesel or electric motors, supports the bucket and hoist-coupler assembly from the boom. The dragrope is used to draw the bucket assembly horizontally. By skillful maneuver of the hoist and the dragropes the bucket is controlled for various operations. A schematic of a large dragline bucket system is shown below.
History
The dragline was invented in 1904 by John W. Page (as a partner of the firm Page & Schnable Contracting) for use in digging the Chicago Canal. By 1912, Page realized that building draglines was more lucrative than contracting, so he created the Page Engineering Company to build draglines. Page built its first crude walking dragline in 1923. These used legs operated by rack and pinion on a separate frame that lifted the crane. The body was then pulled forward by chain on a roller track and then lowered again.[1] Page developed the first diesel engines exclusively for dragline application in 1924. Page also invented the arched dragline bucket, a design still commonly used today by draglines from many other manufacturers, and in the 1960s pioneered an archless bucket design. With its walking mechanism badly behind that of competitor Monighan (see below), Page updated their mechanism to an eccentric drive in 1935. This much improved mechanism gave a proper elliptical motion and was used until 1988. Page modernized its draglines further with the 700 series in 1954. Page's largest dragline was the Model 757 delivered to the Obed Mine near Hinton, Alberta in 1983. It featured a 75-yard bucket on a 298-foot boom and an operating weight of 4,500 tons. In 1988, Harnischfeger Corporation (P&H Mining Equipment) purchased Page Engineering Company.
Harnischfeger Corporation was established as P&H Mining in 1884 by Alonzo Pawling and Henry Harnischfeger. In 1914, P&H introduced the world's first gasoline engine powered dragline. In 1988, Page was acquired by Harnischfeger which makes the P&H line of shovels, draglines, and cranes. P&H's largest dragline is the 9030C with a 160-yard bucket and up to a 425-foot boom. File:Marion 111-M Dragline at New Athens, Ohio.ogv In 1907, Monighan's Machine Works of Chicago became interested in manufacturing draglines when local contractor John W. Page placed an order for hoisting machinery to install one. In 1908, Monighan changed its name to the Monighan Machine Company. In 1913, a Monighan engineer named Oscar Martinson invented the first walking mechanism for a dragline.[2][3][4] The device, known as the Martinson Tractor, was installed on a Monighan dragline, creating the first walking dragline. This gave Monighan a significant advantage over other draglines and the company prospered. The cam mechanism was further improved in 1925 by eliminating the drag chains for the shoes and changing to a cam wheel running in an oval track. This gave the shoe a proper elliptical motion.[5][6] The first dragline using the new mechanism was the 3-W available in 1926. So popular were these machines that the name Monighan became a generic term for dragline. In the early 1930s, Bucyrus-Erie began purchasing shares of Monighan stock with Monighan's approval. Bucyrus purchased a controlling interest and the joint company became known as Bucyrus-Monighan until the formal merger in 1946. The first walking dragline excavator in the United Kingdom was used at the Wellingborough iron quarry in 1940.[7]
Ransomes & Rapier was founded in 1869 by four engineers to build railway equipment and other heavy works. In 1914 they started building two small Steam shovels as a result of a customer request. The rope operated crowd system they built for this was patented[8] and later sold to Bucyrus. After WWI, demand for excavators increased and in 1924 they reached an agreement to build Marion draglines from 1 to 8 cubic yards capacity. In 1927, they built Type-7 1-yard and Type-460 1.5-yard models. The deal to build Marion machines ended in 1936. R&R began building their own designs with the Type-4120 followed by the 4140 of 3.5 cubic yards. In 1958 the Ramsomes & Rapier division was sold to Newton, Chambers & Co. Ltd of Sheffield, which was combined with their NCK Crane & Excavator division. This became NCK-Rapier. The walking dragline division of NCK-Rapier was acquired by Bucyrus in 1988.
The Marion Power Shovel Company (established in 1880) built its first walking dragline with a simple single-crank mechanism in 1939. Its largest dragline was the 8950 sold to Amax Coal Company in 1973. It featured a 150-cubic yard bucket on a 310-foot boom and weighed 7,300 tons. Marion was acquired by Bucyrus in 1997.
Bucyrus Foundry and Manufacturing Company entered the dragline market in 1910 with the purchase of manufacturing rights for the Heyworth-Newman dragline excavator. Their "Class 14" dragline was introduced in 1911 as the first crawler mounted dragline. In 1912 Bucyrus helped pioneer the use of electricity as a power source for large stripping shovels and draglines used in mining. An Italian company, Fiorentini, produced dragline excavators from 1919 licensed by Bucyrus. After the merger with Monighan in 1946, Bucyrus began producing much larger machines using the Monighan walking mechanism such as the 800 ton 650-B which used a 15-yard bucket. Bucyrus' largest dragline was Big Muskie built for the Ohio Coal Company in 1969. This machine featured a 220-yard bucket on a 450-foot boom and weighed 14,500 tons. Bucyrus was itself acquired by heavy equipment and diesel engine maker, Caterpillar, in 2011. Caterpillar's largest dragline is the 8750 with a 169-yard bucket, 435-foot boom, and 8,350 ton weight.
The market for draglines began shrinking rapidly after the boom of the 1960s and 1970s which led to more mergers. P&H's acquisition of Page in 1988 along with Bucyrus' acquisition of Ransomes & Rapier in 1988 and Marion in 1997 cut the number of worldwide suppliers of heavy draglines by more than half. Today, P&H and Caterpillar are the only remaining manufacturers of large draglines.
Other manufacturers
Heavy Engineering Corporation Limited was the first Indian company to manufacture a walking dragline of 31-yard bucket capacity. HEC makes up to a 44-yard bucket. For comparison, this would be comparable to Caterpillar's Small Draglines 8000 series with a 42-yard bucket. HEC has supplied fifteen draglines to the Indian mining industry.[9]
Operation
In a typical cycle of excavation, the bucket is positioned above the material to be excavated. The bucket is then lowered and the dragrope is then drawn so that the bucket is dragged along the surface of the material. The bucket is then lifted by using the hoist rope. A swing operation is then performed to move the bucket to the place where the material is to be dumped. The dragrope is then released causing the bucket to tilt and empty. This is called a dump operation.
On crane-type draglines, the bucket can also be 'thrown' by winding up to the jib and then releasing a clutch on the drag cable. This would then swing the bucket like a pendulum. Once the bucket had passed the vertical, the hoist cable would be released thus throwing the bucket. On smaller draglines, a skilled operator could make the bucket land about one-half the length of the jib further away than if it had just been dropped. On larger draglines, this is not a common practice.
Draglines have different cutting sequences. The first is the side cast method using offset benches; this involves throwing the overburden sideways onto blasted material to make a bench. The second is a key pass. This pass cuts a key at the toe of the new highwall and also shifts the bench further towards the low-wall. This may also require a chop pass if the wall is blocky. A chop pass involves the bucket being dropped down onto an angled highwall to scale the surface. The next sequence is the slowest operation, the blocks pass. However, this pass moves most of the material. It involves using the key to access to bottom of the material to lift it up to spoil or to an elevated bench level. The final cut if required is a pull back, pulling material back further to the low-wall side.[10]
Draglines in mining
A large dragline system used in the open pit mining industry costs approximately US$50–100 million. A typical bucket has a volume ranging from 40 to 80 cubic yards (30 to 60 cubic metres), though extremely large buckets have ranged up to 220 cubic yards (168 cubic meters).[11] The length of the boom ranges from 45 to 100 metres (148 to 328 ft). In a single cycle, it can move up to 450 tonnes of material.
Most mining draglines are not diesel-powered like most other mining equipment. Their power consumption on order of several megawatts is so great[quantify] that they have a direct connection to the high-voltage grid at voltages of between 6.6 and 22 kV. A typical[further explanation needed] dragline weighing 4000 to 6000 tons, with a 55-cubic-metre bucket, can use up to 6 megawatts during normal digging operations. Because of this, many (possibly apocryphal) stories[example needed] have been told about the blackout-causing effects of mining draglines. For instance, there is a long-lived story[according to whom?] that, back in the 1970s, if all seven draglines at Peak Downs Mine (a very large BHP coal mine in central Queensland, Australia) turned simultaneously, they would black out all of North Queensland. However even now,[when?] if they have been shut down, they are always restarted one at a time due to the immense power requirements of startup.[citation needed]
In all but the smallest of draglines, movement is accomplished by "walking" using feet or pontoons, as caterpillar tracks place too much pressure on the ground, and have great difficulty under the immense weight of the dragline. Maximum speed is only at most a few metres per minute,[12] since the feet must be repositioned for each step.[13] If travelling medium distances (about 30–100 km), a special dragline carrier can be brought in to transport the dragline. Above that distance, disassembly is generally required. But mining draglines due to their reach can work a large area from one position and do not need to constantly move along the face like smaller machines.
Limitations
The primary limitations of draglines are their boom height and boom length, which limits where the dragline can dump the waste material. Another primary limitation is their dig depth, which is limited by the length of rope the dragline can utilize. Inherent with their construction, a dragline is most efficient excavating material below the level of their base. While a dragline can dig above itself, it does so inefficiently and is not suitable to load piled up material (as a rope shovel or wheel loader can).
Despite their limitations, and their extremely high capital cost, draglines remain popular with many mines, due to their reliability, and extremely low waste removal cost.
Notable examples
The coal mining dragline known as Big Muskie, owned by the Central Ohio Coal Company (a division of American Electric Power), was the world's largest mobile earth-moving machine, weighing nearly 13,000 tonnes and standing nearly 22 stories tall.[14] It operated in Muskingum County, in the U.S. state of Ohio from 1969 to 1991, and derived power from a 13,800 volt electrical supply. It was dismantled for $700,000 worth of recycled metal in 1999.
The British firm of Ransomes & Rapier produced a few large (1400-1800 ton) excavators, the largest in Europe at the time (1960s). Power was from internal combustion engines driving electric generators. One, named SUNDEW, was used in a quarry from 1957 to 1974. After its working life at the first site in Rutland was finished it walked 13 miles or 20 kms to a new working life at Corby; the walk took 9 weeks. Sundew was then scrapped from January to June 1987.
Smaller draglines were also commonly used before hydraulic excavators came into common use, the smaller draglines are now rarely used other than on river and gravel pit works. The small machines were of a mechanical drive with clutches. Firms such as Ruston and Bucyrus made models such as the RB10 which were popular for small building works and drainage work. Several of these can still be seen in the English Fens of Cambridgeshire, Lincolnshire and parts of Norfolk. Ruston's are a company also associated with drainage pumping engines. Electric drive systems were only used on the larger mining machines, most modern machines use a diesel-hydraulic drive, as machines are seldom in one location long enough to justify the cost of installing a substation and supply cables.
Technological advances
Draglines, unlike most equipment used in earth-moving, have remained relatively unchanged in design and control systems for almost 100 years. Over the last few years, some advances in dragline systems and methodologies have occurred.
Automation
Researchers at CSIRO in Australia have a long-term research project[15] into automating draglines. Mining automation teams at QCAT, a CSIRO division; have been developing the automation technology since 1994. Automated systems include cruise control and Digital Terrain Mapping. Working solutions include the proof-of-concept dragline swing cruise control on a Tarong BE1370.[16]
Simulation software
Since draglines are typically large, complicated and very expensive, training new operators can be a tricky process. In the same way that flight simulators have developed to train pilots, mining simulator software has been developed to assist new operators in learning how to control the machines.
UDD
UDD stands for universal dig-dump. It represents the first fundamental change to draglines for almost a century, since the invention of the 'miracle hitch'. Instead of using two ropes (the hoist rope and the drag rope) to manipulate the bucket, a UDD machine uses four ropes, two hoist and two drag. This allows the dragline operator to have much greater selectivity in when to pick up the bucket, and in how the bucket may be dumped. UDD machines generally have higher productivity than a standard dragline, but often have greater mechanical issues. Within the mining industry, there is still much debate as to whether UDD improvements justify their costs.
See also
- Bucket wheel excavator – alternative mining machine
- Excavator – generic class of machine of which draglines are a sub class
- Power shovel – type of mining machine (also called a front shovel)
- Steam shovel – earliest type of mining excavator
References
- ↑ Editors (29 July 1916). A walking excavator. p. 249.
- ↑ Martinson, Oscar J., "Excavator-Tractor.", US patent 1095464, issued 5 May 1914, assigned to Monighan Machine Co.
- ↑ Martinson, Oscar J., "Tractor.", US patent 1101459, issued 23 June 1914, assigned to Monighan Machine Co.
- ↑ Martinson, Oscar J., "Excavator-Tractor.", US patent 1101460, issued 23 June 1914, assigned to Monighan Machine Co.
- ↑ Martinson, Oscar J., "Traction Mechanism.", US patent 1591764, issued 6 July 1926, assigned to Monighan Machine Co.
- ↑ Martinson, Oscar J., "Traction Machine.", US patent 1627984, issued 10 May 1927, assigned to Monighan Machine Co.
- ↑ Template:Quine ironstone
- ↑ Bowtell, William John, "Improvements in or relating to Luffing Cranes.", GB patent 110458, issued 25 October 1917, assigned to Ransomes & Rapier Ltd.
- ↑ "Heavy Engineering Corporation Limited, Ranchi, India". https://hecltd.com/draglines.php.
- ↑ Mirabediny, H.; Baafi, E. (1998-01-01). "Dragline Digging Methods in Australian Strip Mines – A Survey". Coal Operators' Conference. https://ro.uow.edu.au/coal/278.
- ↑ Keith Haddoc, "Extreme Mining Machines – stripping shovels and draglines", pub by MBI, Appendix 4 Tables of capacities page 127 ISBN:0-7603-0918-3
- ↑ "Maid Marian's journey becomes a 'drag'" The Daily Gleaner (10 October 2008) accessed 1 November 2008]
- ↑ "Paradise for Sidewalk Superintendents" Popular Mechanics, October 1947, p. 153-157, detailed drawings and photos of dragline operation
- ↑ "The Big Muskie – Remembering the walking giant". http://little-mountain.com/bigmuskie/.
- ↑ CSIRO research project
- ↑ "Dragline Automation" Dr Jonathan Roberts CSIRO (11 December 2009) accessed 19 December 2011
- K. Pathak, K. Dasgupta, A. Chattopadhyay, "Determination of the working zone of a dragline bucket – A graphical approach", Doncaster, The Institution of mining engineers, 1992.
- Peter Ridley, Peter Corke, "Calculation of Dragline bucket pose under gravity loading", Mechanism and machine theory, Vol. 35, 2000.
External links
 |