Medicine:Restrictive dermopathy
| Restrictive dermopathy | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Hyperkeratosis-contracture syndrome, Lethal restrictive dermopathy |
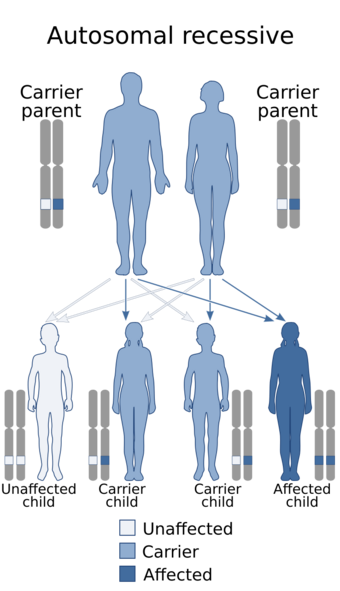 | |
| Restrictive dermopathy is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner[1] | |
Restrictive dermopathy (RD) is a rare, lethal autosomal recessive skin condition characterized by syndromic facies, tight skin, sparse or absent eyelashes, and secondary joint changes.[2]:563
Mechanism
Restrictive dermopathy (RD) is caused either by the loss of the gene ZMPSTE24, which encodes a protein responsible for the cleavage of farnesylated prelamin A into mature non-farnesylated lamin, or by a mutation in the LMNA gene. This results in the accumulation of farnesyl-prelamin A at the nuclear membrane.[3] Mechanistically, restrictive dermopathy is somewhat similar to Hutchinson–Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS), a disease where the last step in lamin processing is hindered by a mutation that causes the loss of the ZMPSTE24 cleavage site in the lamin A gene.[citation needed]
Diagnosis
Treatment
See also
- Relapsing linear acantholytic dermatosis
- List of cutaneous conditions
- Lamellar ichthyosis – Possible differential diagnosis
References
- ↑ "OMIM Entry - # 275210 - RESTRICTIVE DERMOPATHY, LETHAL" (in en-us). https://omim.org/entry/275210.
- ↑ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN:0-7216-2921-0.
- ↑ "Prelamin A farnesylation and progeroid syndromes". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (52): 39741–39745. December 2006. doi:10.1074/jbc.R600033200. PMID 17090536.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
 |

