Chemistry:Dess–Martin oxidation
| Dess–Martin oxidation | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Daniel Benjamin Dess James Cullen Martin |
| Reaction type | Organic redox reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| Organic Chemistry Portal | dess-martin-oxidation |
| RSC ontology ID | RXNO:0000256 |
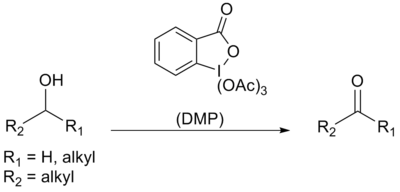
The Dess–Martin oxidation is an organic reaction for the oxidation of primary alcohols to aldehydes and secondary alcohols to ketones using Dess–Martin periodinane.[1][2] It is named after the American chemists Daniel Benjamin Dess and James Cullen Martin who developed the periodinane reagent in 1983.
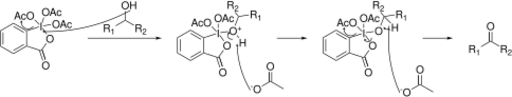
The reaction uses a hypervalent iodine reagent[2] similar to 2-iodoxybenzoic acid to selectively and mildly oxidize alcohols to aldehydes or ketones. The reaction is commonly conducted in chlorinated solvents such as dichloromethane or chloroform.[2] The reaction can be done at room temperature and is quickly complete. Many other functional groups will not be affected by this reaction.
The Dess–Martin oxidation may be preferable to other oxidation reactions as it is very mild, avoids the use of toxic chromium reagents, does not require large excess or co-oxidants, and for its ease of work up.
The reaction produces two equivalents of acetic acid. It can be buffered with pyridine or sodium bicarbonate in order to protect acid-labile compounds.
The rate of oxidation can be increased by the addition of water to the reaction mixture.[3]
References
- ↑ Dess, Daniel B.; Martin, James Cullen (1983). "Readily accessible 12-I-5 oxidant for the conversion of primary and secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones". J. Org. Chem. 48 (22): 4155–4156. doi:10.1021/jo00170a070.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Carey, Francis A.; Sundberg, Richard J. (2007). Advanced Organic Chemistry: Part B: Reactions and Synthesis (5th ed.). New York: Springer. p. 1072. ISBN 978-0387683546.
- ↑ Meyer, Stephanie D.; Schreiber, Stuart L. (1994). "Acceleration of the Dess-Martin Oxidation by Water". J. Org. Chem. 59 (24): 7549–7552. doi:10.1021/jo00103a067.
 |