Chemistry:Primary carbon
From HandWiki
Short description: Carbon atom bound to one other carbon in a molecule
| Primary Carbon |
|---|
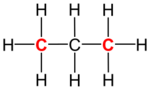
|
| Structural formula of propane (C 3H 8; primary carbons are highlighted red) |
In organic chemistry, a primary carbon is a carbon atom which is bound to only one other carbon atom.[1] It is thus at the end of a carbon chain. In case of an alkane, three hydrogen atoms are bound to a primary carbon (see propane in the figure on the right). A hydrogen atom could also be replaced by a hydroxy group (–OH), which would make the molecule a primary alcohol.[2]
| primary carbon | secondary carbon | tertiary carbon | quaternary carbon | |
| General structure (R = Organyl group) |
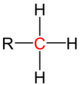
|

|

|

|
| Partial Structural formula |

|

|

|

|
References
- ↑ Smith, Janice Gorzynski (2011). "Chapter 4 Alkanes" (in en) (Book). Organic chemistry (3rd ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill. p. 116. ISBN 978-0-07-337562-5. http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/007340277x/student_view0/index.html. Retrieved 2018-06-26.
- ↑ Hans Peter Latscha, Uli Kazmaier, Helmut Alfons Klein (2016) (in German), Organische Chemie: Chemie-Basiswissen II (7. Auflage ed.), Berlin: Springer Spektrum, p. 40, ISBN 978-3-662-46180-8
 |

