Chemistry:Vinyl propionate
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethenyl propanoate | |
| Other names
Vinyl propanoate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H8O2 | |
| Molar mass | 100.117 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.917 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Boiling point | 95 °C (203 °F; 368 K) |
| 6.5 mL/L | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H225, H315, H319 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P264, P280, P302+352, P303+361+353, P305+351+338, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P370+378, P403+235, P501 | |
| Flash point | −2 °C (28 °F; 271 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
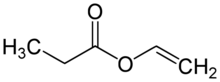
Vinyl propionate is the organic compound with the formula CH3CH2CO2CH=CH2. This colorless liquid is the ester of propionic acid and vinyl alcohol. It is used to produce poly(vinyl propionate) as well as copolymers with acrylate esters, vinyl chloride, and vinyl acetate, some of which are used in paints. The compound resembles vinyl acetate.[1]
Since vinyl alcohol is not available, vinyl propionate is produced by the addition of propionic acid to acetylene. The reaction is catalyzed by carbon and zinc salts.
References
- ↑ G. Roscher (2007). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a27_419. ISBN 978-3527306732.
 |

