Chemistry:Taurochenodeoxycholic acid
From HandWiki
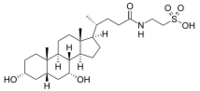
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(3α,7α-Dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-amido)ethane-1-sulfonic acid
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
2-{(4R)-4-[(1R,3aS,3bR,4R,5aS,7R,9aS,9bS,11aR)-4,7-Dihydroxy-9a,11a-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-1-yl]pentanamido}ethane-1-sulfonic acid | |
| Other names
12-Deoxycholyltaurine; 12-Desoxycholyltaurine; Chenodeoxycholyltaurine; Chenyltaurine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C26H45NO6S | |
| Molar mass | 499.71 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Taurochenodeoxycholic acid is a bile acid formed in the liver of most species, including humans, by conjugation of chenodeoxycholic acid with taurine.[1] It is secreted into bile and then into the intestine.[2] It is usually ionized at physiologic pH. However, although it can be crystallized as the sodium salt.
It acts as a detergent to solubilize fats in the small intestine and is itself absorbed by active transport in the terminal ileum.[3]
It is used as a cholagogue and choleretic.
See also
- Tauroursodeoxycholic acid, an epimer
- See article about Taurodeoxycholic acid as an interferent in Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) mass spectrometry analysis.
References
- ↑ Hofmann AF (1999). "The continuing importance of bile acids in liver and intestinal disease". Arch. Intern. Med. 159 (22): 2647–58. doi:10.1001/archinte.159.22.2647. PMID 10597755.
- ↑ "Characterization of fasted-state human intestinal fluids collected from duodenum and jejunum". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 58 (8): 1079–89. August 2006. doi:10.1211/jpp.58.8.0009. PMID 16872555.
- ↑ "Micelle formation by bile salts. Physical-chemical and thermodynamic considerations". Archives of Internal Medicine 130 (4): 506–27. October 1972. doi:10.1001/archinte.1972.03650040040005. PMID 4562149.
 |

