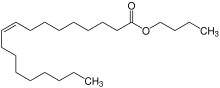
Chemistry:Butyl oleate
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H42O2 | |
| Molar mass | 338.576 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P264+265Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P319Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P321, P332+317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P337+317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P362+364Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Butyl oleate is a fatty acid ester and an organic chemical found in liquid form. It has the formula C22H42O2 and the CAS Registry Number 142-77-8.[2] It is REACH registered and produced or imported into the European Union with the EC number of 205-559-6.
Synthesis and reactions
It is formed by the condensation of oleic acid and butanol often using an enzyme as catalyst or other biobased catalysts.[3][4][5] Ionic liquids may also be used as the catalyst.[6] It undergoes the Bouveault–Blanc reduction with oleyl alcohol and butanol as the products.[7]
Alternative names
It is also known as Butyl cis-9-octadecenoate, Oleic acid butyl ester, butyl 9-octadecenoate and 1-butyl oleate. The IUPAC name is butyl (Z)-octadec-9-enoate.[8]
Uses
It has approval for use as a food additive in Europe[9] and also the US by the FDA.[10] Various other uses include as a lubricant and lubricant additive,[11] paints and coatings additive, and as a plasticizer especially for PVC.[12][13] Similar to other fatty acid esters, it has found use in biodiesel and as a fuel additive.[14]
See also
- Ethyl oleate
- Oleate
References
- ↑ "Butyl oleate" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5354342#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ "CAS Common Chemistry". https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=142-77-8.
- ↑ Orrego, Carlos Eduardo; Valencia, Jesús Sigifredo; Zapata, Catalina (2009-05-01). "Candida rugosa Lipase Supported on High Crystallinity Chitosan as Biocatalyst for the Synthesis of 1-Butyl Oleate" (in en). Catalysis Letters 129 (3): 312–322. doi:10.1007/s10562-009-9857-6. ISSN 1572-879X.
- ↑ Linko, Y.-Y.; Rantanen, O.; Yu, H. -C.; Linko, P. (1992-01-01). "Factors Affecting Lipase Catalyzed n-Butyl Oleate Synthesis". in Tramper, J.; Vermüe, M. H.; Beeftink, H. H. et al.. Biocatalysis in Non-Conventional Media. Progress in Biotechnology. 8. Elsevier. pp. 601–608. doi:10.1016/b978-0-444-89046-7.50087-4. ISBN 9780444890467.
- ↑ Leitgeb, M.; Knez, ž. (November 1990). "The influence of water on the synthesis of n‐butyl oleate by immobilized Mucor miehei lipase" (in en). Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society 67 (11): 775–778. doi:10.1007/BF02540490. ISSN 0003-021X.
- ↑ Zhou, Ningning; Yang, Liancheng; Wang, Yuehan; Ding, Yunlong (2022-08-01). "N-butyl oleate catalyzed- synthesized by triethylamine citrate lonic liquid". Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2321 (1): 012022. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/2321/1/012022. ISSN 1742-6588. Bibcode: 2022JPhCS2321a2022Z.
- ↑ Wang, Zerong, ed (2009). "109. Bouveault–Blanc Reduction". Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents. pp. 493–496. doi:10.1002/9780470638859.conrr109. ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8.
- ↑ PubChem. "Butyl oleate" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5354342.
- ↑ "EU Commission Implementing Regulation adopting the list of flavouring substances" (in en). 2012-10-01. http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg_impl/2012/872/oj/eng.
- ↑ "Inventory of Food Contact Substances Listed in 21 CFR" (in en-US). https://www.cfsanappsexternal.fda.gov/scripts/fdcc/index.cfm?set=IndirectAdditives&id=BUTYLOLEATE.
- ↑ Dailey, Oliver D.; Prevost, Nicolette T.; Strahan, Gary D. (July 2008). "Synthesis and Structural Analysis of Branched‐Chain Derivatives of Methyl Oleate" (in en). Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society 85 (7): 647–653. doi:10.1007/s11746-008-1235-9. ISSN 0003-021X.
- ↑ Riser, G. R.; Bloom, F. W.; Witnauer, L. P. (March 1964). "Evaluation of butyl stearate, butyl oleate, butyl ricinoleate, and methyl oleate as poly(vinyl chloride) plasticizers" (in en). Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society 41 (3): 172–174. doi:10.1007/BF03024639. ISSN 0003-021X.
- ↑ Ghamgui, Hanen; Karra-Chaâbouni, Maha; Gargouri, Youssef (2004-09-01). "1-Butyl oleate synthesis by immobilized lipase from Rhizopus oryzae: a comparative study between n-hexane and solvent-free system". Enzyme and Microbial Technology 35 (4): 355–363. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2004.06.002. ISSN 0141-0229.
- ↑ Lee, Inmok; Johnson, Lawrence A.; Hammond, Earl G. (October 1995). "Use of branched‐chain esters to reduce the crystallization temperature of biodiesel" (in en). Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society 72 (10): 1155–1160. doi:10.1007/BF02540982. ISSN 0003-021X.
 |

