Chemistry:Fensulfothion
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
O,O-Diethyl O-[4-(methanesulfinyl)phenyl] phosphorothioate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H17O4PS2 | |
| Molar mass | 308.35 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Brown liquid or yellow oil[1] |
| Density | 1.20 g/mL (20°C)[1] |
| 0.2% (25°C) | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | combustible[1] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
none[1] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.1 mg/m3[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D.[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
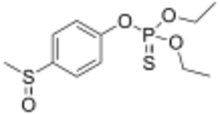
Fensulfothion is an organophosphorus compound with the formula CH
2S(O)C
6H
4OP(S)(OC
2H
5)
2. It is an insecticide and nematicide that acts by inhibiting the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. Chemically, it is classified as a thiophosphate.[2] It is widely used on corn, onions, rutabagas, pineapple, bananas, sugar cane, sugar beets, pea nuts, etc.
Safety
It is highly toxic and listed as an extremely hazardous substance.[3]
External links
- Fensulfothion in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0284". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0284.html.
- ↑ Metcalf Deceased, Robert L.; Horowitz, Abraham Rami (2014). "Insect Control, 2. Individual Insecticides". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. pp. 1–94. doi:10.1002/14356007.s14_s01. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.
- ↑ Appendix A List of Extremely Hazardous Chemicals
 |

