Chemistry:Aglycone
|
|
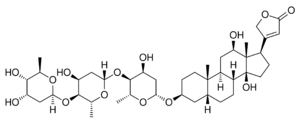
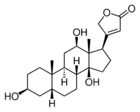
| Chemical structures of digoxin (top) and its aglycone digoxigenin (bottom) |
An aglycone (aglycon[1] or genin) is the chemical compound remaining after the glycosyl group on a glycoside is replaced by a hydrogen atom.[2] For example, the aglycone of a cardiac glycoside would be a steroid molecule.
Detection
A way to identify aglycone is proposed to extract it from Agave spp. by using H-NMR and Heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC) experiments. The HMBC experiment can be combined with other techniques such as mass spectrometry to further examine the structure and the function of aglycone.[3]
Samples of glycones and glycosides from limonoids can be simultaneously quantified through a high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method, where a binary solvent system and a diode array detector separate and detect them at a sensitivity of 0.25-0.50 µg.[4]
Clinical significance
A study on molecular markers in human aortic endothelial cells published that aglycone stopped cell migration but not monocyte adhesion, which is the initial step of atherosclerotic plaque formation.[5] Another study exploring the benefits of extra virgin olive oil consumption in preventing age-related neurodegenerative diseases found aglycone greatly increased the cognitive performance of mice. The aglycone-fed mice displayed strong autophagic reactions, mTOR regulation, and reduced plaque deposits and ß-amyloid levels.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ "Nomenclature of carbohydrates (IUPAC Recommendations 1996).". Pure and Applied Chemistry 68 (10): 1919–2008. January 1996. doi:10.1351/pac199668101919. http://www.chem.qmul.ac.uk/iupac/2carb/33.html. "2-Carb-33".
- ↑ IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology. 67 (2nd ed.). 1997. p. 1312.
- ↑ "Features in the NMR spectra of the aglycones of Agave spp. saponins. HMBC method for aglycone identification (HMAI)". Phytochemical Analysis 32 (1): 38–61. January 2021. doi:10.1002/pca.2946. PMID 32515107.
- ↑ "Simultaneous determination of citrus limonoid aglycones and glucosides by high performance liquid chromatography". Analytica Chimica Acta 590 (2): 180–186. May 2007. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2007.03.029. PMID 17448343.
- ↑ "Ellagitannin metabolites, urolithin A glucuronide and its aglycone urolithin A, ameliorate TNF-α-induced inflammation and associated molecular markers in human aortic endothelial cells". Molecular Nutrition & Food Research 56 (5): 784–796. May 2012. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201100677. PMID 22648625.
- ↑ Ohno, Masuo, ed (2013-08-08). "The polyphenol oleuropein aglycone protects TgCRND8 mice against Aß plaque pathology". PLOS ONE 8 (8): e71702. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0071702. PMID 23951225. Bibcode: 2013PLoSO...871702G.
External links
 |

