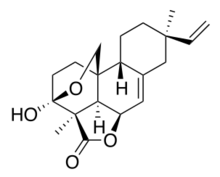
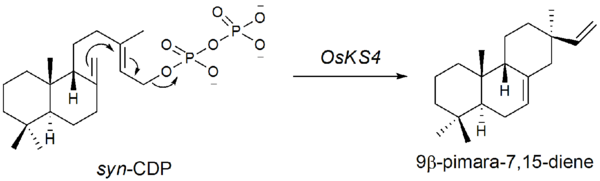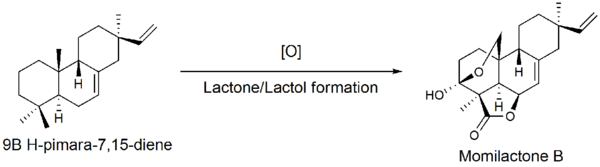Chemistry:Momilactone B
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(3S-(3α,3β,5aβ,8α,10aα,10bβ,10cβ))-8-Ethenyl-3a,5a,7,8,9,10,10a,10c-octahydro-3a,8-dimethyl-,4H-3,10b-ethano-1H,3H-benzo[f]furo[4,3,2-de]-2-benzopyran-4-one
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H26O4 | |
| Molar mass | 330.424 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 242 °C (468 °F; 515 K) (decomp) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Momilactone B is an allelopathic agent produced from the roots of rice (Oryza sativa L.) (100 mg from 200 kg dry rice husk).[1] It has been shown to be produced in high concentrations by the roots of rice seedlings.[2] The production of momilactone B has also been induced in response to infection by blast fungus (Pyricularia oryzae) or irradiated with UV light.[3] More recently it has been shown to be a potential chemotherapeutic agent against human colon cancer.[4]
Biosynthesis
Of the 15 phytoalexins that have been isolated from rice, 14, including momilactone B, are diterpenes commonly biosynthesized from geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGDP). Research on the synthetic pathway for momilactone B has found it involves a set of enzymes that are encoded by genes located on chromosome 4.[citation needed]
The first step in the biosynthesis of momilactone B is the cyclization of GGDP to syn-copalyl diphosphate (syn-CDP), a type B[clarification needed] cyclization. This is initiated by the addition of a proton to the terminal olefin bond of GGDP. The genes encoding for syn-CDP synthase was found by Otomo et al.. in 2004.[5] This was labeled as OsCyc1 (Oryza sativa Cyclase 1). According to the rice genome database, OsCyc1 corresponds to OsCPS4 (AL662933) found in chromosome 4 (14.3cM) discovered by Sakamoto et al.. in 2004.[6]
The second step is the cyclization of syn-CDP to 9β-pimara-7,15-diene. This step is initiated by the elimination of the diphosphate group, a type A[clarification needed] cyclization. The genes encoding for the type A cyclase were found by Otomo et al.. in 2004.[7] It is suggested that OsKS4, located on chromosome 4 (14.3cM) is one of the genes responsible for phytoalexin biosynthesis. After UV-radiation, OsKS4 mRNA levels rise drastically in response to the attack.
Further oxidation of the 9β-pimara-7,15-diene compound followed by lactone and lactol formation yields momilactone B. Though the gene sequence of these oxidations is unknown, P450 monooxygenase genes have been identified near the cyclase genes on chromosome 4.
Stereochemistry
The stereochemistry reported by Kato et al. in 1973[1] is different than that shown in the biosynthesis references. The stereochemistry of momilactone B shown here is based on the biosynthesis references.[5][6][7] There are no known papers correcting the stereochemistry from the isolation paper.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Kato, T.; Kabuto, C.; Sasaki, N.; Tsunagawa, M.; Aizawa, H.; Fujita, K.; Kato, Y.; Kitahara, Y. (1973). "Momilactones, Growth Inhibitors from Rice, Oryza Sativa L.". Tetrahedron Lett. 14 (39): 3861–3864. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)87058-1.
- ↑ Toyomasu, T.; Kagahara, T.; Okada, K.; Koga, J.; Hasegawa, M.; Mitsuhashi, W.; Sassa, T.; Yamane, H. (2008). "Diterpene Phytoalexins are Biosynthesized in and Exuded from the Roots of Rice Seedlings". Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 72 (2): 562–567. doi:10.1271/bbb.70677. PMID 18256463.
- ↑ Cartwright, D. W.; Langcake, P.; Pryce, R. J.; Leworthy, D. P.; Ride, J. P. (1981). "Isolation and Characterization of Two Phytoalexins from Rice as Momilactones A and B". Phytochemistry 20 (3): 535–537. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)84189-8. Bibcode: 1981PChem..20..535C.
- ↑ Kim, S.; Park, H.; Park, E.; Lee, S. (2007). "Cytotoxic and Antitumor Activity of Momilactone B from Rice Hulls". J. Agric. Food Chem. 55 (5): 1702–1706. doi:10.1021/jf062020b. PMID 17326606.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Otomo, K.; Kenmoku, H.; Oikawa, H.; König, W. A.; Toshima, H.; Mitsuhashi, W.; Yamane, H.; Sassa, T. et al. (2004). "Biological functions of ent- and syn-copalyl diphosphate synthases in rice: key enzymes for the branch point of gibberellin and phytoalexin biosynthesis". Plant J. 39 (6): 886–893. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02175.x. PMID 15341631.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Sakamoto, T.; Miura, K.; Itoh, H.; Tatsumi, T.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Ishiyama, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Agrawal, G. K. et al. (2004). "An Overview of Gibberellin Metabolism Enzyme Genes and Their Related Mutants in Rice". Plant Physiol. 134 (4): 1642–1653. doi:10.1104/pp.103.033696. PMID 15075394.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Otomo, K.; Kanno, Y.; Motegi, A.; Kenmoku, H.; Yamane, H.; Mitsuhashi, W.; Oikawa, H.; Toshima, H. et al. (2004). "Diterpene Cyclases Responsible for the Biosynthesis of Phytoalexins, Momilactones A, B, and Oryzalexins A-F in Rice". Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 68 (9): 2001–2006. doi:10.1271/bbb.68.2001. PMID 15388982.
 |