Astronomy:SZ Piscium
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Pisces |
| Right ascension | 23h 13m 23.778s[2] |
| Declination | 02° 40′ 31.60″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 7.18[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K1IV + F8V + ?[4] |
| Variable type | EA/DS/RS[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 12.00±2[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 23.624[2] mas/yr Dec.: 26.346[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 10.6705 ± 0.1864[2] mas |
| Distance | 306 ± 5 ly (94 ± 2 pc) |
| Orbit[4] | |
| Primary | K star |
| Companion | F star |
| Period (P) | 3.96566356 d |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 15.2 R☉[6] |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0 (fixed) |
| Inclination (i) | 69.75° |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 74.2 km/s |
| Semi-amplitude (K2) (secondary) | 103.98 km/s |
| Details | |
| K star | |
| Mass | 1.74[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 6.0[6] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 12.3[6] L☉ |
| Temperature | 4,910[4] K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 3.0±0.6[4] km/s |
| F star | |
| Mass | 1.33[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.52[6] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 3.98[6] L☉ |
| Temperature | 6,090[4] K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 67.7±1.0[4] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
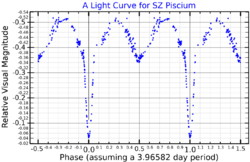
SZ Piscium is a suspected triple star[4] system in the equatorial constellation of Pisces. The inner pair form a double-lined spectroscopic binary with an orbital period of 3.966 days.[8] It is a detached Algol-type eclipsing binary of the RS Canum Venaticorum class with a subgiant component. (This means the pair have a close but separated orbit with the stars eclipsing one another, and the primary component is an evolving star showing star spots and other magnetic activity.) The system is too faint to be readily visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 7.18.[3] It is located at a distance of approximately 306 light years based on parallax measurements.[2]
The variability of this star was reported by A. Jensch in 1934, who published the first elements.[9] In 1956 the spectrum of the system was examined by N. G. Roman, who found the cooler component is the brighter and more evolved.[10] The system was studied by G. A. Bakos and J. F. Heard in 1958, who found a magnitude of 7.72 for the primary eclipse minimum and 7.30 for the secondary. They refined the class estimates, finding the primary is probably a K1IV subgiant in close orbit with an F8V main sequence star.[11] In 1972, H. L. Atkins and D. S. Hall included it on a list of RS Canum Venaticorum type variable systems and showed it has an infrared excess.[12]
S. Jakate and associates in 1976 found that the period of luminosity variation is changing over time. They discovered strong emission in the H and K lines of the K star and noted that it showed intrinsic variability.[8] The system displayed unusual episodes of emission and variation in the Hα line, which was interpreted by astronomers as ejected material possibly forming a transient disk.[13] The orbital period of the system varies in a 56 year cycle with an amplitude of 4.3×10−4 d, which may be explained by influences of the stellar wind and magnetic activity.[4]
Significant star spot activity was found all over the K-type star, with variations in the total spot coverage observed over time.[6] It is estimated to be filling 85% of its Roche lobe due to the gravitational influence of the secondary. The rotation period of this star is several times slower than its orbital period, while the rotation of the F-type star is synchronous.[4] Changes in radial velocity of the system over time suggest it is a triple star system,[6] with the tertiary component having ~90% of the mass of the Sun and an orbital period of 1,283±10 days.[4]
References
- ↑ Eaton, J. A.; Scaltriti, F.; Cerruti-Sola, M.; Sarma, M. B. K.; Ausekar, B. D.; Catalano, S.; Rodono, M. (March 1982). "Light curves of SZ Piscium for 1977 and 1978". Astrophysics and Space Science 82 (2): 289–306. doi:10.1007/BF00651440. Bibcode: 1982Ap&SS..82..289E. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00651440. Retrieved 24 June 2022.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Brown, A. G. A. (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 649: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657. Bibcode: 2021A&A...649A...1G. Gaia EDR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Samus', N. N et al. (2017), "General catalogue of variable stars", Astronomy Reports, GCVS 5.1 61 (1): 80, doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085, Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 4.9 Xiang, Yue et al. (February 2016), "The first Doppler images of the eclipsing binary SZ Piscium", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 456 (1): 314–322, doi:10.1093/mnras/stv2642, Bibcode: 2016MNRAS.456..314X.
- ↑ Karataș, Yüksel et al. (2004), "Kinematics of chromospherically active binaries and evidence of an orbital period decrease in binary evolution", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 349 (3): 1069–1092, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.07588.x, Bibcode: 2004MNRAS.349.1069K.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 Eaton, Joel A.; Henry, Gregory W. (March 2007), "The Distribution of Activity on the RS CVn-Type Star SZ Piscium", The Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific 119 (853): 259–273, doi:10.1086/516603, Bibcode: 2007PASP..119..259E.
- ↑ "SZ Psc". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=SZ+Psc.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Jakate, S. et al. (April 1976), "Eclipsing binary system SZ Piscium", Astronomical Journal 81: 250–256, doi:10.1086/111880, Bibcode: 1976AJ.....81..250J.
- ↑ Kang, Young Woon et al. (October 2003), "Chromospheric activity and unique solution of SZ Psc", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 344 (4): 1227–1232, doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2003.06909.x, Bibcode: 2003MNRAS.344.1227K.
- ↑ Roman, Nancy G. (March 1956), "Spectral Types of Some Eclipsing Binaries", Astrophysical Journal 123: 246, doi:10.1086/146155, Bibcode: 1956ApJ...123..246R.
- ↑ Bakos, G. A.; Heard, J. F. (February 1958), "The eclipsing system, SZ Psc", Astronomical Journal 63: 302, doi:10.1086/107661, Bibcode: 1958AJ.....63Q.302B.
- ↑ Atkins, H. L.; Hall, D. S. (October 1972), "Infrared excesses in eclipsing binaries of the RS Canum Venaticorum type", Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific 84: 638, doi:10.1086/129349, Bibcode: 1972PASP...84..638A.
- ↑ Ramsey, L. W.; Nations, H. L. (December 1981), "On the nature of H alf outbursts in the RS CVn binary SZ Psc", Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific 93: 732–734, doi:10.1086/130917, Bibcode: 1981PASP...93..732R.
Further reading
- Cao, Dongtao et al. (June 2020), "Further Investigation on Chromospheric and Prominence Activity of the RS Canum Venaticorum Star SZ Piscium", The Astronomical Journal 159 (6): 15, doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ab8f90, 292, Bibcode: 2020AJ....159..292C.
- Cao, Dongtao et al. (January 2019), "Prominence activation, optical flare, and post-flare loops on the RS Canum Venaticorum star SZ Piscium", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 482 (1): 988–998, doi:10.1093/mnras/sty2768, Bibcode: 2019MNRAS.482..988C.
- Drake, S. A. et al. (2015), "The Swift Detection of a Large Flare from the RS CVn Binary SZ Psc", GRB Coordinates Network, Circular Service 17304 (1): p. 1, Bibcode: 2015GCN.17304....1D.
- Cao, Dong-Tao; Gu, Sheng-Hong (February 2012), "New observations of chromospheric and prominence activity on the RS CVn-type binary SZ Piscium", Astronomy & Astrophysics 538: 4, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201118184, A130, Bibcode: 2012A&A...538A.130C.
- Negoro, H. et al. (November 2011), "MAXI/GSC detection of a possible flare from the RS CVn type star SZ Psc", The Astronomer's Telegram 3737: 1, Bibcode: 2011ATel.3737....1N.
- Wang, Xiao-Liang et al. (June 2010), "Orbital Period Change of the Eclipsing Binary System SZ Piscium", Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan 62 (3): 671–674, doi:10.1093/pasj/62.3.671, Bibcode: 2010PASJ...62..671W.
- Zhang, L. -Y.; Gu, S. -H. (August 2008), "Chromospheric activity on the RS Canum Venaticorum binary SZ Piscium", Astronomy and Astrophysics 487 (2): 709–716, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200809688, Bibcode: 2008A&A...487..709Z, https://www.aanda.org/10.1051/0004-6361:200809688/pdf.
- Lanza, A. F. et al. (September 2001), "Long-term starspot evolution, activity cycle and orbital period variation of SZ Piscium", Astronomy and Astrophysics 376 (3): 1011–1030, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20011038, Bibcode: 2001A&A...376.1011L.
- Antonopoulou, E. et al. (November 1995), "Photoelectric Observations of SZ Psc During 1993-1994", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 4262 (1): 1, Bibcode: 1995IBVS.4262....1A.
- Kalimeris, A. et al. (January 1995), "An orbital period study of SZ Piscium", Astronomy and Astrophysics 293: 371–376, Bibcode: 1995A&A...293..371K.
- Doyle, J. G. et al. (November 1994), "Surface inhomogeneities on SZ Piscium", Astronomy and Astrophysics 291: 135–142, Bibcode: 1994A&A...291..135D.
- Doyle, J. G. et al. (March 1994), "Ultraviolet flare activity on the eclipsing binary SZ Piscium", Astronomy and Astrophysics 283: 522–524, Bibcode: 1994A&A...283..522D.
- Danezis, E. et al. (January 1992), "The Ultraviolet Spectrum of the Binary System Sz-Piscium", Astrophysics and Space Science 187 (2): 307–318, doi:10.1007/BF00643397, Bibcode: 1992Ap&SS.187..307D.
- Thompson, K. (December 1987), "Photometric Observations on SZ Psc", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 3119 (1): 1, Bibcode: 1987IBVS.3119....1T.
- Bakos, Gustav; Tremko, Josef (November 1987), "The Light Curve Analysis of SZ PISCIUM", Bulletin of the Astronomical Institute of Czechoslovakia 38: 356, Bibcode: 1987BAICz..38..356B.
- Scaltriti, F. et al. (December 1985), "Some Comments on the Minima of the RS CVn Type Eclipsing Binaries CQ Aur, RU Cnc, VV Mon and SZ Psc", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 2841 (1): 1, Bibcode: 1985IBVS.2841....1S.
- Percy, J. R. (June 1985), "A note on two RS Canum Venaticorum stars : LX Persei and SZ Piscium", Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada 79: 113–118, Bibcode: 1985JRASC..79..113P.
- Antonopoulou, E.; Williams, P. M. (June 1984), "Infrared photometry of the RS CVn binaries. IV. SZ Piscium", Astronomy and Astrophysics 135: 61–65, Bibcode: 1984A&A...135...61A.
- Huenemoerder, D. P.; Ramsey, L. W. (April 1984), "Hydrogen-alpha observations of RS Canum Venaticorum stars. III. The eclipsing systems AR Lacertae and SZ Piscium", Astronomical Journal 89: 549–558, doi:10.1086/113547, Bibcode: 1984AJ.....89..549H.
- Tumer, O. et al. (February 1980), "B V Light Curves of SZ Psc", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 1741 (1): 1, Bibcode: 1980IBVS.1741....1T.
- Okazaki, Akira (February 1979), "Photoelectric Observations of SZ Piscium", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 1560 (1): 1, Bibcode: 1979IBVS.1560....1O.
- Catalano, S. et al. (May 1978), "The Orbital Period Variation of SZ Psc", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 1427 (1): 1, Bibcode: 1978IBVS.1427....1C.
- Eaton, J. A. (July 1977), "Further Light Curve Variations of SZ Piscium", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 1297 (1): 1, Bibcode: 1977IBVS.1297....1E.
- Jensch, A. (August 1934), "Ergebnisse photographischer und visueller Beobachtungen an 7 Veräderlichen", Astronomische Nachrichten 252 (24): 393, doi:10.1002/asna.19342522403, Bibcode: 1934AN....252..393J. As '35.1934 Piscium'.
 |