Finance:African Economic Community
The African Economic Community (AEC) is an organization of African Union states establishing grounds for mutual economic development among the majority of African states. The stated goals of the organization include the creation of free trade areas, customs unions, a single market, a central bank, and a common currency (see African Monetary Union) thus establishing an economic and monetary union.
Pillars
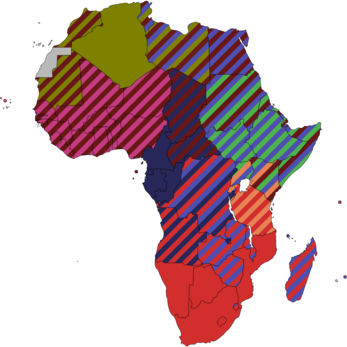
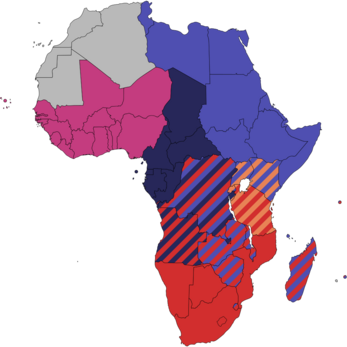
Currently there are multiple regional blocs in Africa, also known as Regional Economic Communities (RECs), many of which have overlapping memberships. The RECs consist primarily of trade blocs and, in some cases, some political and military cooperation. Most of these RECs form the "pillars" of AEC, many of which also have an overlap in some of their member states. Due to this high proportion of overlap it is likely that some states with several memberships will eventually drop out of one or more RECs. Several of these pillars also contain subgroups with tighter customs and/or monetary unions of their own:
These pillars and their corresponding subgroups are as follows:
| Pillars | Subgroups |
|---|---|
| Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD) | |
| Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) | |
| East African Community (EAC) | |
| Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS/CEEAC) | Economic and Monetary Community of Central Africa (CEMAC) |
| Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) | West African Economic and Monetary Union (UEMOA) West African Monetary Zone (WAMZ) |
| Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD) | |
| Southern African Development Community (SADC) | Southern African Customs Union (SACU) Common Monetary Area (CMA) |
| Arab Maghreb Union (UMA) |
Pillar membership
|
|
| ||||||||||||
|
|
|
1 The UMA (Arab Maghreb Union) does not participate in the AEC so far, because of opposition by Morocco
Overlaps illustrated
Other blocs
Other African regional blocs, not participating in the AEC framework (many of them predating AEC) are:
- Greater Arab Free Trade Area (GAFTA) (an organization of most Middle Eastern states, including those outside Africa)
- Economic Community of the Great Lakes Countries (CEPGL)
- Indian Ocean Commission (COI)
- Liptako-Gourma Authority (LGA)
- Mano River Union (MRU)
Their membership is as follows:
| GAFTA 1 | CEPGL | COI | LGA | MRU |
|---|---|---|---|---|
2005 membership:
Joined later:
|
1976 membership:
|
1984 membership:
|
1970 membership:
|
1973 membership:
Joined later:
|
1 Only African GAFTA members are listed.
GAFTA and MRU are the only blocs not currently stalled.
Goals
The AEC founded through the Abuja Treaty, signed in 1991 and entered into force in 1994 is envisioned to be created in six stages:
- (completed in 1999) Creation of regional blocs in regions where such do not yet exist
- (completed in 2007) Strengthening of intra-REC integration and inter-REC harmonisation
- (completed in 2021) Establishing of a free trade area and customs union in each regional bloc
- (to be completed in 2023) Establishing of a continent-wide customs union (and thus also a free trade area)
- (to be completed in 2025) Establishing of a continent-wide African Common Market (ACM)
- (to be completed in 2028) Establishing of a continent-wide economic and monetary union (and thus also a currency union) and Parliament
- End of all transition periods: 2034 at the latest
Stages progress
as of September 2007
- Stage 1: Completed, only Arab Maghreb Union members and Sahrawi Republic not participating. Somalia is participating, but no practical implementation yet.
- Stage 2: Steady progress, nothing factual to check.
- Stage 3:
| Regional blocs - pillars of the African Economic Community (AEC) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activity | CEN-SAD | COMESA | EAC | ECCAS | ECOWAS | IGAD | SADC | UMA | ||||
| CEMAC | Common | UEMOA | WAMZ | Common | SACU | Common | ||||||
| Free Trade Area | stalled | progressing 1 | fully in force | fully in force | proposed for 2007 ? | fully in force | proposed | stalled | fully in force | progressing 2 | stalled | |
| Customs Union | stalled | proposed for 2008 | fully in force | fully in force | proposed for 2011 ? | fully in force | proposed for 2007 | stalled | fully in force | proposed for 2010 | stalled | |
1 Members not yet participating: DR Congo (in talks to join), Eritrea, Ethiopia, Seychelles (in talks to join), Swaziland (on derogation until SACU gives permission for Swaziland to join the FTA), Uganda (to join very soon)[1]
2 Members not yet participating: Angola, DR Congo, Seychelles [2]
- Stage 4: In March 2018, 49 African countries signed the African Continental Free Trade Agreement paving the way for a continent-wide free trade area. The continental free trade area became operational in July 2019, after 22 ratifications.[4][5] As of 2021, 34 signatories have effectively become parties of the treaty.
- Stage 5: no progress yet
- Stage 6: no progress yet
Overall progress
| Activities | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regional bloc | Free Trade Area | Economic and monetary union | Free Travel | Political pact | Defence pact | ||||
| Customs Union | Single Market | Currency Union | Visa-free | Border-less | |||||
| AEC | Partially In Force | proposed for 2023 | proposed for 2023 | proposed for 2028 | proposed for 2023 | proposed for 2023 | proposed for 2028 | proposed for 2028 | |
| CEN-SAD | proposed for 2010 | ||||||||
| COMESA | in force 1 | proposed for 2008 | ? | proposed for 2018 | |||||
| EAC | in force | in force | proposed for 2015 | proposed for 2024 | proposed for 2018[6] | ? | proposed for 2023 | ||
| ECCAS | CEMAC | in force | in force | ? | in force | ||||
| Common | proposed for 2007 ? | proposed for 2011 ? | proposed | proposed | proposed | ? | in force | ||
| ECOWAS | UEMOA | in force | in force | proposed[7] | in force | ||||
| WAMZ | ? | proposed for 2012 | |||||||
| Common | proposed 2 | proposed for 2007 | proposed[8] | proposed | in force 1 | proposed | proposed | in force | |
| IGAD | |||||||||
| SADC | SACU | in force | in force | de facto in force 1 | ? | ||||
| Common[3][yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}] | proposed for 2008 3 | proposed for 2010 | proposed for 2015 | proposed for 2016 | |||||
| UMA | |||||||||
1 not all members participating yet
2 telecommunications, transport and energy - proposed
3 sensitive goods to be covered from 2012
African Free Trade Zone
The African Free Trade Zone (AFTZ) was announced on Wednesday October 22, 2008 by the heads of Southern African Development Community (SADC), the Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) and the East African Community (EAC).
In May 2012 the idea was extended to also include ECOWAS, ECCAS and AMU.[9]
See also
- African Economic Outlook
- Economy of Africa
- Economy of the African Union
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "SADC, COMESA and the EAC: Conflicting regional and trade agendas". Institute for Global Dialogue. October 2008. http://www.igd.org.za/publications/occasional-papers/item/download/32.
- ↑ "African integration is great but has its hurdles". New Vision. 26 May 2010. http://www.newvision.co.ug/D/8/20/720784.
- ↑ Mugisha, Ivan R. (2010-08-20). "Rwanda back to Central Africa bloc, 10 years on". https://www.theeastafrican.co.ke/news/Rwanda--back-to-Central-Africa-bloc-10-years-on-/2558-3352178-nsmc6b/index.html.
- ↑ Kede, Shoshana (2 April 2019). "Africa free trade agreement gets last ratification from Gambia". https://africanbusinessmagazine.com/uncategorised/continental/africa-free-trade-agreement-gets-last-ratification-from-gambia/.
- ↑ "AfCFTA Agreement secures minimum threshold of 22 ratification as Sierra Leone and the Saharawi Republic deposit instruments". 29 April 2019. https://au.int/en/pressreleases/20190429/afcfta-agreement-secures-minimum-threshold-22-ratification-sierra-leone-and.
- ↑ Ligami, Christabel (2017-04-17). "East Africa e-passports to be issued in 2018". https://www.theeastafrican.co.ke/news/East-Africa-e-passports-to-be-issued-in-2018/2558-3892934-5nf7g5z/index.html.
- ↑ WT/COMTD/N/11
- ↑ WT/COMTD/N/21
- ↑ Africa free trade zone in operation by 2018
Sources
- A single African currency in our time?
- African leaders agree to form single market
- African Union Official Website
- South African webpage on RECs
- Pan-African Perspective
 |