Chemistry:Macrophage-activating lipopeptide 2
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
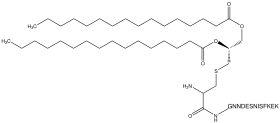
S-[(2R)-2,3-bis[(1-oxohexadecyl)oxy]propyl]-L-cysteinylglycyl-L-asparaginyl-L-asparaginyl-L-α-aspartyl-L-α-glutamyl-L-seryl-L-asparaginyl-L-isoleucyl-L-seryl-L-phenylalanyl-L-lysyl-L-α-glutamyl-L-Lysine
| |
| Other names
MALP-2, S-[2,3-bis(Palmityloxy)-(2R)-propyl-cysteinyl-GNNDESNISFKEK
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | XGNNDESNISFKEK |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C99H167N19O30S | |
| Molar mass | 2135.59 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Macrophage-activating lipopeptide 2 (MALP-2) is a lipopeptide Toll-like receptor (TLR)-2 and 6 agonist. It is used in immunological research to simulate Mycoplasma bacterial infections and activate immune cells. MALP-2 holds promise as a novel vaccine adjuvant due to its activation of TLRs.[1][2] It also promotes vascular, bone, and wound healing.[3][4]
Structure
MALP-2 has the structure S-2,3-bis(palmityloxy)-(2R)-propyl-cysteinyl-GNNDESNISFKEK and is a post-translationally modified CGNNDESNISFKEK peptide in which in the N-terminus cysteine residue sidechain is linked to a diacylglycerol moiety where the two acyl groups are both derived from palmitic acid.[5]
Discovery
MALP-2 was initially named mycoplasma-derived high-molecular-weight material (MDHM) and, as the name suggests, had originally been isolated from Mycoplasma fermentans as an amphiphilic molecule with macropage-activating properties. This discovery helped explain how Mycoplasma bacteria can provoke immune responses despite lacking a cell wall.[6][7]
References
- ↑ "Lipopeptides for Vaccine Development". Bioconjugate Chemistry 32 (8): 1472–1490. August 2021. doi:10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.1c00258. PMID 34228433.
- ↑ "Self-adjuvanting lipopeptide vaccines". Current Medicinal Chemistry 15 (5): 506–516. 2008. doi:10.2174/092986708783503249. PMID 18289006.
- ↑ "Pushing the envelope: Immune mechanism and application landscape of macrophage-activating lipopeptide-2". Frontiers in Immunology 14: 1113715. January 2023. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1113715. PMID 36761746.
- ↑ "Macrophage-activating lipopeptide-2 (MALP-2) induces a localized inflammatory response in rats resulting in activation of brain sites implicated in fever". Brain Research 1205: 36–46. April 2008. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.02.021. PMID 18353287.
- ↑ "MALP-2". Enzo Life Sciences, Inc.. https://www.enzolifesciences.com/ALX-162-027/malp-2/.
- ↑ "Purification and partial biochemical characterization of a Mycoplasma fermentans-derived substance that activates macrophages to release nitric oxide, tumor necrosis factor, and interleukin-6". Infection and Immunity 62 (9): 3801–3807. September 1994. doi:10.1128/iai.62.9.3801-3807.1994. PMID 8063396.
- ↑ "Isolation, structure elucidation, and synthesis of a macrophage stimulatory lipopeptide from Mycoplasma fermentans acting at picomolar concentration". The Journal of Experimental Medicine 185 (11): 1951–8. June 1997. doi:10.1084/jem.185.11.1951. PMID 9166424.
 |

