Biology:Koelliker's glass lizard
| Koelliker's glass lizard | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Family: | Anguidae |
| Genus: | Hyalosaurus Günther, 1873 |
| Species: | H. koellikeri
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hyalosaurus koellikeri Günther, 1873
| |
| |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
Koelliker's glass lizard (Hyalosaurus koellikeri), also called commonly the Moroccan glass lizard, is a species of lizard in the family Anguidae.[2] The species is native to western North Africa.
Etymology
The specific name, koellikeri, is in honor of Swiss histologist Albert von Kölliker.[3]
Geographic range
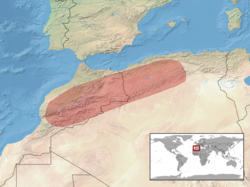
H. koellikeri is found in Algeria and Morocco.[2]
Habitat
The natural habitats of Koelliker's glass lizard are temperate forests, shrubland, temperate grassland, and pastureland, at altitudes up to 2,000 m (6,600 ft).[2]
Description
H. koellikeri has no fore limbs, but does have rudimentary hind limbs. Dorsally, it is brownish, with a darker lateral band. Ventrally, it is yellowish.[4]
Taxonomy
Hyalosaurus koellikeri has often been historically included within the genus Ophisaurus, but genetic evidence has shown Hyalosaurus koellikeri to be more closely related to Anguis and Pseudopus than to Ophisaurus.[5]
Reproduction
H. koellikeri is oviparous.[1]
Conservation status
H. koellikeri is threatened by habitat loss.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Species Hyalosaurus koellikeri at The Reptile Database . www.reptile-database.org.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namediucn - ↑ Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. ISBN:978-1-4214-0135-5. (Ophisaurus koellikeri, p. 144).
- ↑ Boulenger (1885).
- ↑ Lavin, Brian R.; Girman, Derek J. (April 2019). "Phylogenetic relationships and divergence dating in the Glass Lizards (Anguinae)". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 133: 128–140. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2018.12.022. PMID 30584918.
Further reading
- Boulenger GA (1885). Catalogue of the Lizards in the British Museum (Natural History). Second Edition. Volume II. ... Anguidae ... London: Trustees of the British Museum (Natural History). (Taylor and Francis, printers). xiii + 497 pp. + Plates I-XXIV. (Ophisaurus koellokeri, new combination, p. 283 + Plate XV, figures 2, 2a, 2b).
- Escoriza D, Comas MM (2011). "Nova cita de Hyalosaurus koellikeri (Squamata: Anguidae) a la regió de Debdou (Nord-est de Marroc)". Butlletí de la Societat Catalana d'Herpetologia 19: 122–124, Figures 1–2. (in Catalan, with an abstract in English).
- Günther A (1873). "Description of a new Saurian (Hyalosaurus) allied to Pseudopus ". Annals and Magazine of Natural History, Fourth Series 11: 351. ("Hyalosaurus Kœllikeri ", new species).
- Sindaco R, Jeremčenko VK (2008). The Reptiles of the Western Palearctic. 1. Annotated Checklist and Distributional Atlas of the Turtles, Crocodiles, Amphisbaenians and Lizards of Europe, North Africa, Middle East and Central Asia. (Monographs of the Societas Herpetologica Italica). Latina, Italy: Edizioni Belvedere. 580 pp. ISBN:978-88-89504-14-7. (Hyalosaurus koellikeri ).
Wikidata ☰ {{{from}}} entry
 |


