Biology:Plectreuridae
| Plectreurid spiders | |
|---|---|

| |
| Male plectreurid | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Chelicerata |
| Class: | Arachnida |
| Order: | Araneae |
| Infraorder: | Araneomorphae |
| Family: | Plectreuridae Simon, 1893 |
| Genera | |
| |
| Diversity | |
| 2 genera, 32 species | |
| |
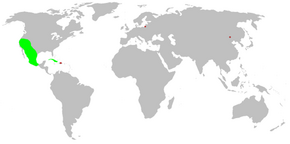
Plectreuridae, also called plectreurid spiders, is a small spider family confined to the Southwestern United States, Mexico,[1] and the Caribbean.[2] Only two living genera are known—the nominate genus Plectreurys and Kibramoa. In the past, the family was more widespread, with the Jurassic genus Eoplectreurys known from China , the Eocene Palaeoplectreurys baltica from Baltic amber and the Miocene Plectreurys pittfieldi from Dominican amber.[3]
These ecribellate, haplogyne spiders build haphazard webs under rocks and dead cacti. Adult males can be found wandering at night.[2] Relatively little is known of their biology. Unlike the sicariids, scytodids, and diguetids, to which they are most closely related, they have eight eyes. In appearance females of Plectreurys resemble those of the larger species of the cribellate Filistatidae. They differ in their eye arrangement and in having the femurs on the first pair of legs bowed. Also, in relativity to body size, they have the largest recognized venom glands, with their multilobular glands taking up up to 50% of their body. [4]
Genera
(As of April 2019), the World Spider Catalog accepts the following genera:[5]
- Kibramoa Chamberlin, 1924 — United States, Mexico
- Plectreurys Simon, 1893 — North America, Cuba, Central America
- †Eoplectreurys Selden & Huang, 2010
- †Palaeoplectreurys Wunderlich, 2004
References
- ↑ Carpenter, T. L.; Bernacky, B. J.; Stabell, E. E. (1991). "Human Envenomization by Plectreurys tristis Simon (Araneae: Plectreuridae): A Case Report". Journal of Medical Entomology 28 (3): 477–478. doi:10.1093/jmedent/28.3.477. PMID 1875380.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Ubick, D. (2005). Spiders of North America: An Identification Manual. American Arachnological Society, Keene (New Hampshire).
- ↑ Selden, P.A.; Huang, D. (2010). "The oldest haplogyne spider (Araneae: Plectreuridae), from the Middle Jurassic of China". Naturwissenschaften 97 (5): 449–59. doi:10.1007/s00114-010-0649-z. PMID 20140419. Bibcode: 2010NW.....97..449S.
- ↑ Mammola, Stefano; Michalik, Peter; Hebets, Eileen A.; Isaia, Marco (31 October 2017). "Record breaking achievements by spiders and the scientists who study them". PeerJ 5: e3972. doi:10.7717/peerj.3972. PMID 29104823.
- ↑ "Family: Plectreuridae Simon, 1893". Natural History Museum Bern. http://www.wsc.nmbe.ch/family/80.
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q11683 entry
 |

