Biology:Aspergillus indologenus
| Aspergillus indologenus | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Eurotiomycetes |
| Order: | Eurotiales |
| Family: | Aspergillaceae |
| Genus: | Aspergillus |
| Species: | A. indologenus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Aspergillus indologenus Frisvad, Varga & Samson (2011)[1]
| |
Aspergillus indologenus is a species of fungus in the genus Aspergillus. It belongs to the group of black Aspergilli which are important industrial workhorses.[2][3][4] A. indologenus belongs to the Nigri section. The species was first described in 2011.[1] It was isolated from soil in India and found to produce insecticidal compounds okaramins A, B, H, and two types of indol-alkaloids which have not been structure elucidated.[1]
The genome of A. indologenus was sequenced and published in 2014 as part of the Aspergillus whole-genome sequencing project – a project dedicated to performing whole-genome sequencing of all members of the genus Aspergillus.[5] The genome assembly size was 38.59 Mbp.[5]
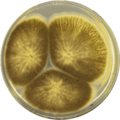
Growth and morphology
Aspergillus indologenus has been cultivated on both Czapek yeast extract agar (CYA) plates and Malt Extract Agar Oxoid® (MEAOX) plates. The growth morphology of the colonies can be seen in the pictures below.
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 "New and revisited species in Aspergillus section Nigri". Studies in Mycology 69 (1): 1–17. June 2011. doi:10.3114/sim.2011.69.01. PMID 21892239.
- ↑ "Genome sequencing and analysis of the versatile cell factory Aspergillus niger CBS 513.88". Nature Biotechnology 25 (2): 221–31. February 2007. doi:10.1038/nbt1282. PMID 17259976.
- ↑ Goldberg, Israel; Rokem, J Stefan; Pines, Ophry (2006). "Organic acids: old metabolites, new themes". Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology 81 (10): 1601–1611. doi:10.1002/jctb.1590.
- ↑ "Determining the Safety of Enzymes Used in Food Processing". Journal of Food Protection 46 (5): 453–468. May 1983. doi:10.4315/0362-028x-46.5.453. PMID 30913657.
- ↑ Jump up to: 5.0 5.1 "Home - Aspergillus indologenus CBS 114.80 v1.0". https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/Aspind1/Aspind1.home.html.
Wikidata ☰ Q60520336 entry
 |