Biology:Ambigolimax
| Ambigolimax | |
|---|---|

| |
| An active Ambigolimax slug in Fremont, California | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Gastropoda |
| Subclass: | Heterobranchia |
| Order: | Stylommatophora |
| Family: | Limacidae |
| Genus: | Ambigolimax Pollonera, 1887[1] |
| Type species | |
| Ambigolimax valentianus (Férussac, 1821)
| |
Ambigolimax is a genus of air-breathing land slugs in the family Limacidae, the keelback slugs.[2] There is still ongoing disagreement whether it is more appropriate to consider Ambigolimax as merely a subgenus of Lehmannia; the evidence for splitting them is phylogenetic trees constructed on the basis of DNA sequences.
Species
The species in the genus are:
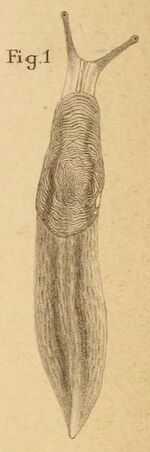
- Ambigolimax valentianus (Férussac, 1821)[3][4] – Valencia slug, threeband garden slug
- Ambigolimax parvipenis Hutchinson, Reise & Schlitt, 2022[5][6]
- Ambigolimax waterstoni Hutchinson, Reise & Schlitt, 2022[5][7]
These species are not reliably distinguishable on the basis of external characters, so identification requires either dissection to reveal the genitalia or DNA sequencing. All three are invasive in various parts of the world.[5]
In addition, Lehmannia melitensis is treated as a species of Ambigolimax by Hutchinson et al. (2022) based on similarity of DNA sequences.[5]
Previous usage of the name Ambigolimax nyctelius has now been shown to refer to several species that had been confused: A. parvipenis, A. waterstoni, and Lehmannia carpatica. Furthermore, the species name nyctelius actually refers to a species of Letourneuxia (family Arionidae).[5][8]
Taxonomic history
Ambigolimax was constructed by Pollonera in 1887[1] to encompass A. valentianus and what he called A. fulvus but is now understood to be Malacolimax tenellus.[9] He considered Ambigolimax as a subgenus of Agriolimax (now Deroceras) in the family Agriolimacidae. In 1926, Hesse transferred it to become a subgenus of Lehmannia in the family Limacidae.[10] Since about 2007 the increasing tendency has been to split Lehmannia s.l. into two genera, Lehmannia s.s. and Ambigolimax. This splitting was based on the genetic evidence that the position of Malacolimax in the phylogenetic tree makes Lehmannia s.l. a paraphyletic group.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Pollonera, Carlo (1887). "Intorno ad alcuni Limacidi europei poco noti". Bollettino dei Musei di Zoologia ed Anatomia Comparata della Reale Università di Torino 2 (21): 1–4, pl. 1. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/11666236.
- ↑ Marshall, B. (2015). Ambigolimax Pollonera, 1887. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=819989 on 2015-04-15
- ↑ Vendetti, J.E.; Burnett, E.; Carlton, L.; Curran, A.T.; Lee, C.; Matsumoto, R.; Mc Donnell, R.; Reich, I. et al. (11 July 2019). "The introduced terrestrial slugs Ambigolimax nyctelius (Bourguignat, 1861) and Ambigolimax valentianus (Férussac, 1821) (Gastropoda: Limacidae) in California, with a discussion of taxonomy, systematics, and discovery by citizen science". Journal of Natural History 53 (25-26): 1607–1632. doi:10.1080/00222933.2018.1536230.
- ↑ "Ambigolimax valentianus (A. Férussac, 1821)". Flanders Marine Institute. https://www.molluscabase.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=819990.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Hutchinson, J.M.C.; Reise, H.; Schlitt, B. (7 July 2022). "Will the real Limax nyctelius please step forward: Lehmannia, Ambigolimax, or Malacolimax? No, Letourneuxia!". Archiv für Molluskenkunde 151 (1): 19–41. doi:10.1127/arch.moll/151/019-041.
- ↑ "Ambigolimax parvipenis Hutchinson, Reise & Schlitt, 2022". Flanders Marine Institute. https://www.molluscabase.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=1593178.
- ↑ "Ambigolimax waterstoni Hutchinson, Reise & Schlitt, 2022". Flanders Marine Institute. https://www.molluscabase.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=1593176.
- ↑ "Ambigolimax nyctelius Hutchinson, Reise & Schlitt, 2022". Flanders Marine Institute. https://www.molluscabase.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=1002614.
- ↑ Altena, C.O. van Regteren (1958). "Notes sur les limaces. 4. Qu’est-ce que Limax fulvus Normand?". Basteria 22 (1): 18–20. https://natuurtijdschriften.nl/pub/596380/BAST1958022001004.pdf.
- ↑ Hesse, P. (1926). "Die Nacktschnecken der palaearktischen Région". Abhandlungen des Archivs für Molluskenkunde 2 (1): 1–152 + 2 pls.
Wikidata ☰ Q20685871 entry
 |

