Biology:White-cheeked pintail
| White-cheeked pintail | |
|---|---|

| |
| Anas bahamensis galapagensis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Anseriformes |
| Family: | Anatidae |
| Genus: | Anas |
| Species: | A. bahamensis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Anas bahamensis | |
| Subspecies | |
| |
The white-cheeked pintail (Anas bahamensis), also known as the Bahama pintail or summer duck,[2] is a species of dabbling duck. It was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his landmark 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae under its current scientific name.[3]
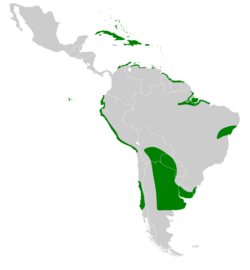
Distribution and habitat
It is found in the Caribbean, South America, and the Galápagos Islands.[4] It occurs on waters with some salinity, such as brackish lakes, estuaries and mangrove swamps.[4]
There are three subspecies:
- A. b. bahamensis—lesser Bahama pintail[2]—in the Caribbean, and a vagrant to southern Florida
- A. b. rubirostris—greater Bahama pintail[2]—in South America; it may be partly migratory, breeding in Argentina and wintering further north.[4]
- A. b. galapagensis—Galápagos pintail[2]—in the Galápagos Islands
Description
Like many southern ducks, the sexes are similar. It is mainly brown with white cheeks and a red-based grey bill (young birds lack the pink). It cannot be confused with any other duck in its range.[4]
Behaviour
The white-cheeked pintail feeds on aquatic plants (such as Ruppia), grass seeds, algae[5][6] and small creatures (such as insects and small aquatic invertebrates)[5][6] obtained by dabbling. The nest is on the ground under vegetation and near water.[4]
Aviculture
It is popular in wildfowl collections, and escapees are frequently seen in a semi-wild condition in Europe. A leucistic (whitish) variant is known in aviculture as the silver Bahama pintail.[2]
Gallery
Two white-cheeked pintails on the Island of Santa Cruz in the Galápagos Islands
Taken in the Galápagos Islands
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Anas bahamensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T22680287A92853819. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22680287A92853819.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22680287/92853819. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Cowell, Dan. "Bahama Pintail / White-cheeked Pintail". Harteman Wildfowl. Jan Harteman. http://www.harteman.nl/omnibus/anseriformes/ducks/bahama-pintail.html.
- ↑ Linnaeus, Carl (1758) (in la). Systema naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Tomus I. Editio decima, reformata. Holmiae. (Laurentii Salvii). pp. 124. "A. grisea, rostro plumbeo: macula laterali fulva, macula alarum viridi luteaque."
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Madge, Steve; Burn, Hilary (1988). Wildfowl: An Identification Guide to the Ducks, Geese and Swans of the World (Helm Identification Guides). Christopher Helm. pp. 224–225. ISBN 0-7470-2201-1.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Anas bahamensis (White-cheeked Pintail)". https://sta.uwi.edu/fst/lifesciences/sites/default/files/lifesciences/images/Anas%20bahamensis%20-%20White-cheeked%20Pintail.pdf.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Anas bahamensis (White-cheeked pintail)". https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Anas_bahamensis/.
External links
- White-cheeked pintail videos, photos, and sounds on the Internet Bird Collection
Wikidata ☰ Q800212 entry
 |










