Biology:Collared plover
| Collared plover | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Charadriiformes |
| Family: | Charadriidae |
| Genus: | Charadrius |
| Species: | C. collaris
|
| Binomial name | |
| Charadrius collaris (Vieillot, 1818)
| |
| |
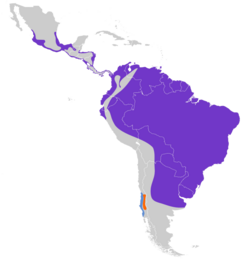
The collared plover (Charadrius collaris) is a small shorebird in the plover family, Charadriidae. It lives along coasts and riverbanks of the tropical to temperate Americas, from central Mexico south to Chile and Argentina .
This small plover is 18 centimetres (7.1 in) long and weighs 35 grams (1.2 oz). Its upperparts are brown and the underparts white in all plumages. Adults have a black breast band. The male has a white forehead, bordered above by a black frontal bar, and below by a black stripe from the bill to the eye. The midcrown and nape are chestnut and the legs are yellow. In flight, the flight feathers are dark with a white wing bar, and the tail shows white sides.
The female collared plover is usually very similar to the male, but some individuals can be sexed by a brown tinge to the black areas. Immature birds lack any black on the head, and the breast band is replaced by brown patches on each side of the chest. The flight call is a sharp metallic pip.
Two sympatric Charadrius species are very similar: The snowy plover is similar in size and structure to this species, but is paler above, has dark legs, and never has a complete breastband. semipalmated plovers are larger, thicker-billed, and has a pale collar. Ironically, it is the lack of a pale collar which gives the collared plover its English language and scientific names.
The collared plover is found on sandy coasts, estuarine mud, inland riverbanks and open sandy savannas. It breeds from Mexico south through Central America and most of South America. It also occurs on some of the southern Caribbean islands, and both Trinidad and Tobago. It appears to be mainly sedentary, although there is some evidence for limited seasonal movements. Collared plovers feed on insects and other invertebrates, which are obtained by a run-and-pause technique, rather than the steady probing of some other wader groups. This species is not particularly gregarious, and seldom forms flocks. It is usually very wary.
The timing of breeding activity varies depending on location: November to December in western Mexico,[2] March to June in Costa Rica,[3] January in Venezuela, and March in the lowlands of Ecuador. The male's courtship display involves fluffing out his breast feathers and running after the female; the species has no known aerial display.[2] The nest is a bare ground scrape well above the tide or flood line on coasts and river shores or islands, or inland, often next to low cover, such as tufts of grass. The clutch is two pale buff eggs, spotted with brown.[3] Like many ground-nesting species, adults perform a broken-wing display to lure presumed threats away from their nest and young.[4]
Footnotes
- ↑ BirdLife International (2020). "Charadrius collaris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020: e.T22693842A163622696. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22693842A163622696.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22693842/163622696. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Hayman, Peter; Marchant, John; Prater, Tony (1986). Shorebirds: an identification guide to the waders of the world. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. p. 296. ISBN 978-0-395-60237-9.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Stiles, F. Gary; Skutch, Alexander Frank (1989). A guide to the birds of Costa Rica. Ithaca: Comstock. p. 139. ISBN 978-0-8014-9600-4.
- ↑ Greeney, Harold F.; Gelis, Rudolphe A.; White, Richard (2004). "Notes on breeding birds from an Ecuadorian lowland forest". Bulletin of the British Ornithologists' Club 124 (1): 28–37. http://depts.washington.edu/nhrg/Greeney,%20Gelis%20%26%20White%202004.pdf. Retrieved 2008-03-27.
References
- ffrench, Richard; O'Neill, John Patton & Eckelberry, Don R. (1991): A guide to the birds of Trinidad and Tobago (2nd edition). Comstock Publishing, Ithaca, N.Y.. ISBN:0-8014-9792-2
- Hilty, Steven L. (2003): Birds of Venezuela. Christopher Helm, London. ISBN:0-7136-6418-5
Wikidata ☰ Q1264712 entry


