Biology:Australasian grebe
| Australasian grebe | |
|---|---|

| |
| A mature Australasian grebe in its breeding plumage | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Podicipediformes |
| Family: | Podicipedidae |
| Genus: | Tachybaptus |
| Species: | T. novaehollandiae
|
| Binomial name | |
| Tachybaptus novaehollandiae (Stephens, 1826)
| |
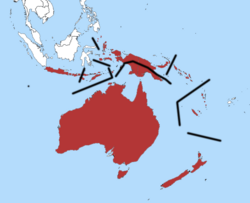
| |
| Distribution of the Australasian grebe with subspecies separated with lines | |
The Australasian grebe (Tachybaptus novaehollandiae) is a small waterbird common on fresh water lakes and rivers in greater Australia, New Zealand and on nearby Pacific islands. At 25–27 cm (9.8–10.6 in) in length, it is one of the smallest members of the grebe family, along with the least grebe and little grebe.
Taxonomy
Subspecies
- Tachybaptus novaehollandiae, (Stephens, 1826)
- Tachybaptus novaehollandiae javanicus, (Mayr, 1943), Java
- Tachybaptus novaehollandiae fumosus, (Mayr, 1943), Talaud & Sangihe Islands
- Tachybaptus novaehollandiae incola, (Mayr, 1943), northern New Guinea
- Tachybaptus novaehollandiae novaehollandiae, (Stephens, 1826), southern New Guinea, Australia , Tasmania & New Zealand
- Tachybaptus novaehollandiae leucosternos, (Mayr, 1931), Vanuatu & New Caledonia
- Tachybaptus novaehollandiae rennellianus, (Mayr, 1943), Rennell Island (Solomon Islands)
Description
Breeding plumage
Both sexes are dark brown above with a glossy-black head and neck and a striking chestnut facial stripe, extending from behind the eye to the base of the neck. The eye is yellow, with a prominent pale yellow face spot below.
Non-breeding plumage
Both sexes are generally duller, with no chestnut stripe, the face spot whiter, and throat and front grey-white. Similar to non-breeding hoary-headed grebes, which share a similar range.
Behaviour
The Australasian grebe is an excellent swimmer and diver, and usually dives immediately when alarmed and swims away under water.
They are not strong flyers and will fly distances only at night, presumably to avoid predators. They tend not to leave their home base if there is sufficient food. If disturbed they will dive and re-surface 10–15 metres away rather than fly.
Both parents will raise the chicks; however, the male will leave after a couple of months when the chicks are about three-quarters grown. Initially the young will ride on the parents back, hidden between their slightly raised wings. When the chicks begin to dive and feed themselves (at about 10 weeks) the mother may leave too, although mothers have been known to return soon after, apparently to check on the chicks.
The parents are very protective and will try to drive away other water birds (ducks, herons) by confronting them and flapping their wings wildly or using their wings to splash water at the intruders.
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Tachybaptus novaehollandiae". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T22696553A93570492. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22696553A93570492.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22696553/93570492. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ↑ "Grebes". International Ornithological Congress. http://www.worldbirdnames.org/BOW/grebes/.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Australasian grebe. |
- BirdLife Species Factsheet
- Australian Museum fact sheet
- Video at the Internet Bird Collection
- A pictorial essay of nesting grebes
Wikidata ☰ Q783361 entry
 |






