Biology:2R hypothesis
The 2R hypothesis or Ohno's hypothesis, first proposed by Susumu Ohno in 1970,[1] is a hypothesis that the genomes of the early vertebrate lineage underwent two complete genome duplications, and thus modern vertebrate genomes reflect paleopolyploidy. The name derives from the 2 rounds of duplication originally hypothesized by Ohno, but refined in a 1994 version, and the term 2R hypothesis was probably coined in 1999. Variations in the number and timings of genome duplications typically still are referred to as examples of the 2R hypothesis.[2]
The 2R hypothesis has been the subject of much research and controversy; however, with growing support from genome data, including the human genome, the balance of opinion has shifted strongly in favour of support for the hypothesis. According to Karsten Hokamp, Aoife McLysaght and Kenneth H. Wolfe,[2] the version of the genome duplication hypothesis from which 2R hypothesis takes its name appears in Holland et al.[3] and the term was coined by Austin L. Hughes.[4]
Ohno's argument
Ohno presented the first version of the 2R hypothesis as part of his larger argument for the general importance of gene duplication in evolution. Based on relative genome sizes and isozyme analysis, he suggested that ancestral fish or amphibians had undergone at least one and possibly more cases of "tetraploid evolution". He later added to this argument the evidence that most paralogous genes in vertebrates do not demonstrate genetic linkage. Ohno argued that linkage should be expected in the case of individual tandem duplications (in which a duplicate gene is added adjacent to the original gene on the same chromosome), but not in the case of chromosome duplications.[5]
Later evidence
In 1977, Schmidtke and colleagues showed that isozyme complexity is similar in lancelets and tunicates, contradicting a prediction of Ohno's hypothesis that genome duplication occurred in the common ancestor of lancelets and vertebrates.[6] However, this analysis did not examine vertebrates, so could say nothing about later duplication events.[7] (Furthermore, much later molecular phylogenetics has shown that vertebrates are more closely related to tunicates than to lancelets, thus negating the logic of this analysis.[8]) The 2R hypothesis saw a resurgence of interest in the 1990s for two reasons. First, gene mapping data in humans and mice revealed extensive paralogy regions - sets of genes on one chromosome related to sets of genes on another chromosome in the same species, indicative of duplication events in evolution.[9] Paralogy regions were generally in sets of four. Second, cloning of Hox genes in lancelet revealed presence of a single Hox gene cluster,[10] in contrast to the four clusters in humans and mice. Data from additional gene families revealed a common one-to-many rule when lancelet and vertebrate genes were compared.[7] Taken together, these two lines of evidence suggest that two genome duplications occurred in the ancestry of vertebrates, after it had diverged from the cephalochordate evolutionary lineage.
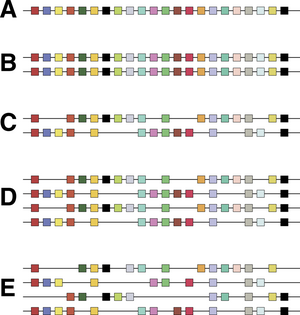
Controversy about the 2R hypothesis hinged on the nature of paralogy regions. It is not disputed that human chromosomes bear sets of genes related to sets of genes on other chromosomes; the controversy centres on whether they were generated by large-scale duplications that doubled all the genes at the same time, or whether a series of individual gene duplications occurred followed by chromosomal rearrangement to shuffle sets of genes together. Hughes and colleagues found that phylogenetic trees built from different gene families within paralogy regions had different shapes, suggesting that the gene families had different evolutionary histories.[12][13] This was suggested to be inconsistent with the 2R hypothesis. However, other researchers have argued that such 'topology tests' do not test 2R rigorously, because recombination could have occurred between the closely related chromosomes generated by polyploidy,[14][15] because inappropriate genes had been compared[16] and because different predictions are made if genome duplication occurred through hybridisation between species.[17] In addition, several researchers were able to date duplications of gene families within paralogy regions consistently to the early evolution of vertebrates, after divergence from amphioxus, consistent with the 2R hypothesis.[18][19] When complete genome sequences became available for vertebrates, Ciona intestinalis and lancelets, it was found that much of the human genome was arranged in paralogy regions that could be traced to large-scale duplications,[20] and that these duplications occurred after vertebrates had diverged from tunicates[11] and lancelets.[21] This would date the two genome duplications to between 550 and 450 million years ago.
The controversy raging in the late 1990s was summarized in a 2001 review of the subject by Wojciech Makałowski, who stated that "the hypothesis of whole genome duplications in the early stages of vertebrate evolution has as many adherents as opponents".[5]
In contrast, a more recent review in 2007 by Masanori Kasahara states that there is now "incontrovertible evidence supporting the 2R hypothesis" and that "a long-standing debate on the 2R hypothesis is approaching the end".[22] Michael Benton, in the 2014 edition of Vertebrate Palaeontology, states, "It turns out that, in places where amphioxus has a single gene, vertebrates often have two, three, or four equivalent genes as a result of two intervening whole-genome duplication events."[23]
Ohnology
Ohnologous genes are paralogous genes that have originated by a process of this 2R duplication. The name was first given in honour of Susumu Ohno by Ken Wolfe.[24] It is useful for evolutionary analysis because all ohnologues in a genome have been diverging for the same length of time (since their common origin in the whole genome duplication).[25][26]
Well-studied ohnologous genes include genes in human chromosome 2, 7, 12 and 17 containing Hox gene clusters, collagen genes, keratin genes and other duplicated genes,[27] genes in human chromosomes 4, 5, 8 and 10 containing neuropeptide receptor genes, NK class homeobox genes and many more gene families,[28][29][30] and parts of human chromosomes 13, 4, 5 and X containing the ParaHox genes and their neighbors.[31] The Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) on human chromosome 6 has paralogy regions on chromosomes 1, 9 and 19.[32] Much of the human genome seems to be assignable to paralogy regions.[33]
References
- ↑ Ohno, Susumu (1970). Evolution by Gene Duplication. London: Allen and Unwin, ISBN:0-04-575015-7.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Hokamp, K; McLysaght, A; Wolfe, KH (2003). "The 2R hypothesis and the human genome sequence". Journal of Structural and Functional Genomics 3 (1–4): 95–110. doi:10.1023/A:1022661917301. PMID 12836689.
- ↑ Holland, PW; Garcia-Fernàndez, J; Williams, NA; Sidow, A (1994). "Gene duplications and the origins of vertebrate development". Development. Supplement: 125–33. PMID 7579513.
- ↑ Hughes, Austin L. (1999). "Phylogenies of developmentally important proteins do not support the hypothesis of two rounds of genome duplication early in vertebrate history". Journal of Molecular Evolution 48 (5): 565–76. doi:10.1007/PL00006499. PMID 10198122. Bibcode: 1999JMolE..48..565H.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Makalowski, Wojciech (2001). "Are we polyploids? A brief history of one hypothesis". Genome Research 11 (5): 667–70. doi:10.1101/gr.188801. PMID 11337465.

- ↑ Schmidtke, Jörg; Weiler, Conrad; Kunz, Brigitte; Engel, Wolfgang (1977). "Isozymes of a tunicate and a cephalochordate as a test of polyploidisation in chordate evolution". Nature 266 (5602): 532–533. doi:10.1038/266532a0. PMID 859619. Bibcode: 1977Natur.266..532S.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Holland, PW (2003). "More genes in vertebrates?". Journal of Structural and Functional Genomics 3 (1–4): 75–84. doi:10.1023/a:1022656931587. PMID 12836687.

- ↑ Delsuc, F; Brinkmann, H; Chourrout, D; Philippe, H (2006). "Tunicates and not cephalochordates are the closest living relatives of vertebrates.". Nature 439 (7079): 965–8. doi:10.1038/nature04336. PMID 16495997. Bibcode: 2006Natur.439..965D. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/halsde-00315436/file/Delsuc-Nature06_HAL.pdf.

- ↑ Lundin, LG (April 1993). "Evolution of the vertebrate genome as reflected in paralogous chromosomal regions in man and the house mouse.". Genomics 16 (1): 1–19. doi:10.1006/geno.1993.1133. PMID 8486346.
- ↑ Garcia-Fernández, J; Holland, PW (Aug 18, 1994). "Archetypal organization of the amphioxus Hox gene cluster.". Nature 370 (6490): 563–6. doi:10.1038/370563a0. PMID 7914353. Bibcode: 1994Natur.370..563G.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Dehal, Paramvir; Boore, Jeffrey L. (2005). "Two Rounds of Whole Genome Duplication in the Ancestral Vertebrate". PLOS Biology 3 (10): e314. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0030314. PMID 16128622.

- ↑ Hughes, AL (May 1999). "Phylogenies of developmentally important proteins do not support the hypothesis of two rounds of genome duplication early in vertebrate history". Journal of Molecular Evolution 48 (5): 565–76. doi:10.1007/PL00006499. PMID 10198122. Bibcode: 1999JMolE..48..565H.
- ↑ Hughes, Austin L.; Friedman, Robert (2003). "2R or not 2R: Testing hypotheses of genome duplication in early vertebrates". Journal of Structural and Functional Genomics 3 (1/4): 85–93. doi:10.1023/A:1022681600462. PMID 12836688.
- ↑ Furlong, RF; Holland, PW (2002). "Were vertebrates octoploid?". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B 357 (1420): 531–44. doi:10.1098/rstb.2001.1035. PMID 12028790.
- ↑ Lynch, VJ; Wagner, GP (2009). "Multiple chromosomal rearrangements structured the ancestral vertebrate Hox-bearing protochromosomes.". PLOS Genetics 5 (1): e1000349. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000349. PMID 19165336.

- ↑ Larhammar, D.; Josephson, M (2002). "The Human Hox-bearing Chromosome Regions Did Arise by Block or Chromosome (or Even Genome) Duplications". Genome Research 12 (1): 1910–1920. doi:10.1101/gr.445702. PMID 12466295.
- ↑ Spring, Jürg (1997). "Vertebrate evolution by interspecific hybridisation – are we polyploid?". FEBS Letters 400 (1): 2–8. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(96)01351-8. PMID 9000502.

- ↑ Abi-Rached, L; Gilles, A; Shiina, T; Pontarotti, P; Inoko, H (2002). "Evidence of en bloc duplication in vertebrate genomes.". Nature Genetics 31 (1): 100–5. doi:10.1038/ng855. PMID 11967531.
- ↑ Castro, LF; Holland, PW (Sep–Oct 2003). "Chromosomal mapping of ANTP class homeobox genes in amphioxus: piecing together ancestral genomes.". Evolution & Development 5 (5): 459–65. doi:10.1046/j.1525-142x.2003.03052.x. PMID 12950625.
- ↑ McLysaght, Aoife; Hokamp, Karsten; Wolfe, Kenneth H. (2002). "Extensive genomic duplication during early chordate evolution". Nature Genetics 31 (2): 200–204. doi:10.1038/ng884. PMID 12032567.
- ↑ Putnam, NH; Butts, T; Ferrier, DE; Furlong, RF; Hellsten, U; Kawashima, T; Robinson-Rechavi, M; Shoguchi, E et al. (2008). "The amphioxus genome and the evolution of the chordate karyotype". Nature 453 (7198): 1064–71. doi:10.1038/nature06967. PMID 18563158. Bibcode: 2008Natur.453.1064P.
- ↑ Kasahara, Masanori (2007). "The 2R hypothesis: an update". Current Opinion in Immunology 19 (5): 547–52. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2007.07.009. PMID 17707623.

- ↑ Benton, Michael (2014). Vertebrate Palaeontology. Wiley. p. 92. ISBN 978-1-118-40764-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=qak-BAAAQBAJ&pg=PT92. Retrieved 19 December 2015.
- ↑ "Robustness--it's not where you think it is". Nature Genetics 25 (1): 3–4. May 2000. doi:10.1038/75560. PMID 10802639.
- ↑ "Ohnologs are overrepresented in pathogenic copy number mutations". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 111 (1): 361–6. January 2014. doi:10.1073/pnas.1309324111. PMID 24368850. Bibcode: 2014PNAS..111..361M.
- ↑ "Ohnologs in the human genome are dosage balanced and frequently associated with disease". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 107 (20): 9270–4. May 2010. doi:10.1073/pnas.0914697107. PMID 20439718. Bibcode: 2010PNAS..107.9270M.
- ↑ "Gene loss and gain in the evolution of the vertebrates". Development 1994: 155–61. 1994. doi:10.1242/dev.1994.Supplement.155. PMID 7579516.
- ↑ "Ancient large-scale genome duplications: phylogenetic and linkage analyses shed light on chordate genome evolution". Molecular Biology and Evolution 15 (9): 1145–59. September 1998. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026022. PMID 9729879.
- ↑ "Early vertebrate chromosome duplications and the evolution of the neuropeptide Y receptor gene regions". BMC Evolutionary Biology 8: 184. June 2008. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-8-184. PMID 18578868.
- ↑ "Evidence for 14 homeobox gene clusters in human genome ancestry". Current Biology 10 (17): 1059–62. September 2000. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(00)00676-X. PMID 10996074.
- ↑ "Breakup of a homeobox cluster after genome duplication in teleosts". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 103 (27): 10369–10372. July 2006. doi:10.1073/pnas.0600341103. PMID 16801555. Bibcode: 2006PNAS..10310369M.
- ↑ "Comparative genomics of the MHC: glimpses into the evolution of the adaptive immune system". Immunity 15 (3): 351–62. September 2001. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(01)00198-4. PMID 11567626.
- ↑ "Extensive genomic duplication during early chordate evolution". Nature Genetics 31 (2): 200–4. June 2002. doi:10.1038/ng884. PMID 12032567.
 |

