Biology:Black-headed parrot
| Black-headed parrot | |
|---|---|

| |
| At Jurong Bird Park, Singapore | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Psittaciformes |
| Family: | Psittacidae |
| Genus: | Pionites |
| Species: | P. melanocephalus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Pionites melanocephalus | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The black-headed parrot (Pionites melanocephalus ; sometimes incorrectly Pionites melanocephala) is a species of bird in subfamily Arinae of the family Psittacidae, the African and New World parrots.[3] Other colloquial names are black-crowned parrot, black-capped parrot, black-headed caique, and for subspecies P. m. pallidus, pallid caique.[4] It is found in Brazil , Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela.[5]
Taxonomy and systematics
The genus Pionites has two species, the black-headed parrot and the white-bellied parrot, according to the South American Classification Committee of the American Ornithological Society, the International Ornithological Committee, and the Clements taxonomy.[6][3][7] However, BirdLife International's Handbook of the Birds of the World splits the white-bellied parrot into three species.[8]
The four systems agree that the black-headed parrot has two subspecies, the nominate P. m. melanocephalus (Linnaeus, 1758), and P. m. pallidus (Berlepsch, 1889).[6][3][7][8]
Description
The black-headed parrot is 21 to 25 cm (8.3 to 9.8 in) long and weighs 130 to 170 g (4.6 to 6.0 oz). The sexes are the same. Adults of the nominate subspecies have a black cap from forehead to nape and a rufous-orange band across their hindneck. They are green from their lores to below their eye, and yellow on their lower face, sides of their neck, and their upper breast. Their back and wings are dull green with dark blue primaries and reddish blue axiillaries. Their lower breast and belly are creamy white and their flanks, thighs, and vent area are apricot yellow. Their tail's top surface is green with yellow feather tips and the lower surface is olive-yellow. Immature birds have pale yellow breasts and bellies. Subspecies P. m. pallidus is similar to the nominate but has a whiter breast and belly and a paler rufous-orange band on the hindneck.[9][10][11][12]
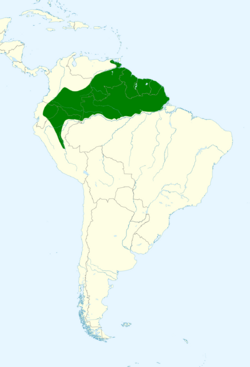
Distribution and habitat
The nominate subspecies of the black-headed parrot is found from southeastern Colombia east through Venezuela and the Guianas and south into Brazil to the Amazon River. Subspecies P. m. pallidus is found east of the Andes in southern Colombia, eastern Ecuador, and northeastern Peru.[3][9] The species inhabits the canopy, clearings, and edges of humid lowland tropical forest of both terra firme and várzea types. It also occurs in secondary forest. In elevation it ranges as high as 1,000 m (3,300 ft) but only in small numbers above 500 m (1,600 ft).[9][10][11][12]
Behavior
Movement
The black-headed parrot is nomadic in French Guiana to follow the pattern of food availability. Its movements elsewhere, if any, have not been documented. The species is typically seen in small flocks of up to about eight individuals.[9][11][12]
Feeding
The black-headed parrot feeds on seeds, fruit, flowers, and leaves.[9] Flocks eat palm leaves, apparently for their mineral content, and do not visit clay licks.[12]
Breeding
The black-headed parrot's nesting season varies widely across its range. It includes April and May in Venezuela, October and November in Suriname, and spans from December to February in French Guiana. It nests in tree cavities and the clutch size is believed to be two to four eggs. In captivity the incubation period is 25 days and fledging occurs 10 weeks after hatch.[9][4]
Vocalization
The black-headed parrot's flight call is " a high-pitched and penetrating squealing "skeeea .. skeeea"[9] also described as "a wheezy or squealing screech, e.g. 'screeéyr, screeyer-screeyer-screeyer'."[11] It is very vocal when perched, where it makes "a variety of calls, some more musical, others rather un-birdlike".[11]
In aviculture
Black-headed parrots are popular in aviculture. The only ways to determine gender of an individual black-headed parrot are surgical sexing and DNA sexing. DNA sexing is safer for the bird than surgical sexing. Black-headed parrots are playful and energetic pets. They need a large cage with many toys and perches (they tend to hop more than fly). Cage minimum should be 24" L X 24" W X 36" H, though the larger the better. Maximum bar spacing is 1". The black-headed parrot can have a tendency to bite, so owners may need to set boundaries early on. However, potential owners should prepare for a bird that uses its beak more often than other parrot species. Some Black-headed parrots will poorly mimic human speech. However, they more commonly mimic other surrounding sounds, such as alarm clocks, smoke detectors, microwave-oven beeps, laughs, car alarms, and whistles. In addition, caiques will combine sounds they have picked up to make new ones.[citation needed]
Status
The IUCN has assessed the black-headed parrot as being of Least Concern. It has a very large range, and though its population size is not known it is believed to be stable. No immediate threats have been identified.[1] It is considered generally common throughout its range, and "vast areas of habitat remain". Though it is a very common cage bird in Venezuela, the international pet trade does not appear to be large.[9]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 BirdLife International (2016). "Black-headed Parrot Pionites melanocephalus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T22686079A93098194. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22686079A93098194.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22686079/93098194. Retrieved 4 March 2023.
- ↑ "Appendices | CITES". https://cites.org/eng/app/appendices.php.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "Parrots, cockatoos". January 2023. https://www.worldbirdnames.org/new/bow/parrots/.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Black-headed Parrot (Pionites melanocephalus)". World Parrot Trust. https://www.parrots.org/encyclopedia/black-headed-parrot.
- ↑ Remsen, J. V., Jr., J. I. Areta, E. Bonaccorso, S. Claramunt, A. Jaramillo, D. F. Lane, J. F. Pacheco, M. B. Robbins, F. G. Stiles, and K. J. Zimmer. 30 January 2023. Species Lists of Birds for South American Countries and Territories. https://www.museum.lsu.edu/~Remsen/SACCCountryLists.htm retrieved 30 January 2023
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Remsen, J. V., Jr., J. I. Areta, E. Bonaccorso, S. Claramunt, A. Jaramillo, D. F. Lane, J. F. Pacheco, M. B. Robbins, F. G. Stiles, and K. J. Zimmer. Version 30 January 2023. A classification of the bird species of South America. American Ornithological Society. https://www.museum.lsu.edu/~Remsen/SACCBaseline.htm retrieved 30 January 2023
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Clements, J. F., T. S. Schulenberg, M. J. Iliff, S. M. Billerman, T. A. Fredericks, J. A. Gerbracht, D. Lepage, B. L. Sullivan, and C. L. Wood. 2021. The eBird/Clements checklist of Birds of the World: v2021. Downloaded from https://www.birds.cornell.edu/clementschecklist/download/ Retrieved 25 August 2021
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 HBW and BirdLife International (2022) Handbook of the Birds of the World and BirdLife International digital checklist of the birds of the world. Version 7. Available at: http://datazone.birdlife.org/userfiles/file/Species/Taxonomy/HBW-BirdLife_Checklist_v7_Dec22.zip retrieved 13 December 2022
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 Collar, N. and P. F. D. Boesman (2020). Black-headed Parrot (Pionites melanocephalus), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (J. del Hoyo, A. Elliott, J. Sargatal, D. A. Christie, and E. de Juana, Editors). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.blhpar4.01 retrieved 4 March 2023
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 van Perlo, Ber (2009). A Field Guide to the Birds of Brazil. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 136. ISBN 978-0-19-530155-7.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 Ridgely, Robert S.; Greenfield, Paul J. (2001). The Birds of Ecuador: Field Guide. II. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. pp. 195. ISBN 978-0-8014-8721-7.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 McMullan, Miles; Donegan, Thomas M.; Quevedo, Alonso (2010). Field Guide to the Birds of Colombia. Bogotá: Fundación ProAves. pp. 62. ISBN 978-0-9827615-0-2.
Further reading
- Parr, M., & Juniper, T. (1998). A Guide to the Parrots of the World. Pica Press, East Sussex. ISBN:1-873403-40-2
- Restall, R., Rodner, C., & Lentino, M. (2006). Birds of Northern South America. Vol. 1 & 2. Helm, London. ISBN:0-7136-7242-0 (vol. 1); ISBN:0-7136-7243-9 (vol. 2)
- Schulenberg, T., Stotz, D. Lane, D., O'Neill, J, & Parker, T. (2007). Birds of Peru. Helm, London. ISBN:978-0-7136-8673-9
- Sigrist, T. (2006). Aves do Brasil – Uma Visão Artistica. ISBN:85-905074-1-6
Wikidata ☰ Q922245 entry
 |






